PGC-1alpha coactivates PDK4 gene expression via the orphan nuclear receptor ERRalpha: a mechanism for transcriptional control of muscle glucose metabolism
- PMID: 16314495
- PMCID: PMC1316952
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.10684-10694.2005
PGC-1alpha coactivates PDK4 gene expression via the orphan nuclear receptor ERRalpha: a mechanism for transcriptional control of muscle glucose metabolism
Abstract
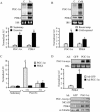
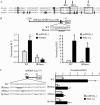
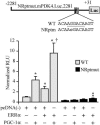
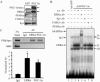
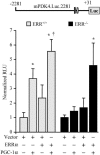
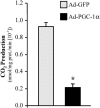
The transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha is a key regulator of energy metabolism, yet little is known about its role in control of substrate selection. We found that physiological stimuli known to induce PGC-1alpha expression in skeletal muscle coordinately upregulate the expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4), a negative regulator of glucose oxidation. Forced expression of PGC-1alpha in C(2)C(12) myotubes induced PDK4 mRNA and protein expression. PGC-1alpha-mediated activation of PDK4 expression was shown to occur at the transcriptional level and was mapped to a putative nuclear receptor binding site. Gel shift assays demonstrated that the PGC-1alpha-responsive element bound the estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha), a recently identified component of the PGC-1alpha signaling pathway. In addition, PGC-1alpha was shown to activate ERRalpha expression. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays confirmed that PGC-1alpha and ERRalpha occupied the mPDK4 promoter in C(2)C(12) myotubes. Additionally, transfection studies using ERRalpha-null primary fibroblasts demonstrated that ERRalpha is required for PGC-1alpha-mediated activation of the mPDK4 promoter. As predicted by the effects of PGC-1alpha on PDK4 gene transcription, overexpression of PGC-1alpha in C(2)C(12) myotubes decreased glucose oxidation rates. These results identify the PDK4 gene as a new PGC-1alpha/ERRalpha target and suggest a mechanism whereby PGC-1alpha exerts reciprocal inhibitory influences on glucose catabolism while increasing alternate mitochondrial oxidative pathways in skeletal muscle.
Figures
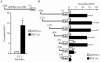

References
-
- Arany, Z., H. He, J. Lin, K. Hoyer, C. Handschin, O. Toka, F. Ahmad, T. Matsui, S. Chin, P.-H. Wu, I. I. Rybkin, J. M. Shelton, M. Manieri, S. Cinti, F. J. Schoen, R. Bassel-Duby, A. Rosenzweig, J. S. Ingwall, and B. M. Spiegelman. 2005. Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α controls the energy state and contractile function of cardiac muscle. Cell Metab. 1:259-271. - PubMed
-
- Baar, K., A. R. Wende, T. E. Jones, M. Marison, L. A. Nolte, M. Chen, D. P. Kelly, and J. O. Holloszy. 2002. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to exercise: rapid increase in the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α. FASEB J. 16:1879-1886. - PubMed
-
- Brandt, J., F. Djouadi, and D. P. Kelly. 1998. Fatty acids activate transcription of the muscle carnitine palmitoyltransferase I gene in cardiac myocytes via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α. J. Biol. Chem. 273:23786-23792. - PubMed
-
- Carter, M. E., T. Gulick, B. D. Raisher, T. Caira, J. A. Ladias, D. D. Moore, and D. P. Kelly. 1993. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 activates medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene transcription by interacting with a complex regulatory element. J. Biol. Chem. 268:13805-13810. - PubMed
-
- Caruso, M., C. Miele, P. Formisano, G. Condorelli, G. Bifulco, A. Oliva, R. Auricchio, G. Riccardi, B. Capaaldo, and F. Beguinot. 1997. In skeletal muscle, glucose storage and oxidation are differentially impaired by the IR1152 mutant receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 272:7290-7297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
