Mutations of the Yku80 C terminus and Xrs2 FHA domain specifically block yeast nonhomologous end joining
- PMID: 16314503
- PMCID: PMC1316971
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.10782-10790.2005
Mutations of the Yku80 C terminus and Xrs2 FHA domain specifically block yeast nonhomologous end joining
Abstract
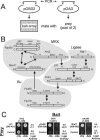
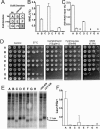
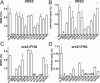
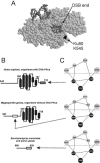
The nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA double-strand break repair requires three protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: MRX (Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2), Ku (Ku70-Ku80), and DNA ligase IV (Dnl4-Lif1-Nej1). Much is known about the interactions that mediate the formation of each complex, but little is known about how they act together during repair. A comprehensive yeast two-hybrid screen of the NHEJ factors of S. cerevisiae revealed all known interactions within the MRX, Ku, and DNA ligase IV complexes, as well as three additional, weaker interactions between Yku80-Dnl4, Xrs2-Lif1, and Mre11-Yku80. Individual and combined deletions of the Yku80 C terminus and the Xrs2 forkhead-associated (FHA) domain were designed based on the latter two-hybrid results. These deletions synergistically blocked NHEJ but not the telomere and recombination functions of Ku and MRX, confirming that these protein regions are functionally important specifically for NHEJ. Further mutational analysis of Yku80 identified a putative C-terminal amphipathic alpha-helix that is both required for its NHEJ function and strikingly similar to a DNA-dependent protein kinase interaction motif in human Ku80. These results identify a novel role in yeast NHEJ for the poorly characterized Ku80 C-terminal and Xrs2 FHA domains, and they suggest that redundant binding of DNA ligase IV facilitates completion of this DNA repair event.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recruitment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Dnl4-Lif1 complex to a double-strand break requires interactions with Yku80 and the Xrs2 FHA domain.Genetics. 2008 Dec;180(4):1809-19. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.095539. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18832348 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment and dissociation of nonhomologous end joining proteins at a DNA double-strand break in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2008 Mar;178(3):1237-49. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.083535. Epub 2008 Feb 3. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18245831 Free PMC article.
-
Promotion of Dnl4-catalyzed DNA end-joining by the Rad50/Mre11/Xrs2 and Hdf1/Hdf2 complexes.Mol Cell. 2001 Nov;8(5):1105-15. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00388-4. Mol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11741545
-
Tying up loose ends: nonhomologous end-joining in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mutat Res. 2000 Jun 30;451(1-2):71-89. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(00)00041-5. Mutat Res. 2000. PMID: 10915866 Review.
-
Non-homologous end-joining factors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2004 Nov;28(5):581-601. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2004.06.001. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15539075 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Plasmodium falciparum DNA Repair Protein Mre11 with an Evolutionarily Conserved Nuclease Function.PLoS One. 2015 May 4;10(5):e0125358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125358. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25938776 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide screens for sensitivity to ionizing radiation identify the fission yeast nonhomologous end joining factor Xrc4.G3 (Bethesda). 2014 May 21;4(7):1297-306. doi: 10.1534/g3.114.011841. G3 (Bethesda). 2014. PMID: 24847916 Free PMC article.
-
Overhang polarity of chromosomal double-strand breaks impacts kinetics and fidelity of yeast non-homologous end joining.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Apr 7;44(6):2769-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw013. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26773053 Free PMC article.
-
Sumoylation influences DNA break repair partly by increasing the solubility of a conserved end resection protein.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jan 8;11(1):e1004899. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004899. eCollection 2015 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25569253 Free PMC article.
-
HDF1 and RAD17 genes are involved in DNA double-strand break repair in stationary phase Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Phys. 2008 Apr;34(1-2):63-71. doi: 10.1007/s10867-008-9105-0. Epub 2008 Aug 13. J Biol Phys. 2008. PMID: 19669493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brachmann, C. B., A. Davies, G. J. Cost, E. Caputo, J. Li, P. Hieter, and J. D. Boeke. 1998. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14:115-132. - PubMed
-
- Chen, L., K. Trujillo, W. Ramos, P. Sung, and A. E. Tomkinson. 2001. Promotion of Dnl4-catalyzed DNA end-joining by the Rad50/Mre11/Xrs2 and Hdf1/Hdf2 complexes. Mol. Cell 8:1105-1115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
