Antagonistic effects of Grg6 and Groucho/TLE on the transcription repression activity of brain factor 1/FoxG1 and cortical neuron differentiation
- PMID: 16314515
- PMCID: PMC1316978
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.10916-10929.2005
Antagonistic effects of Grg6 and Groucho/TLE on the transcription repression activity of brain factor 1/FoxG1 and cortical neuron differentiation
Abstract
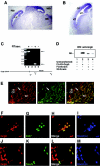
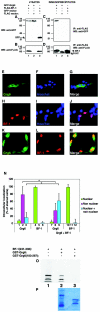
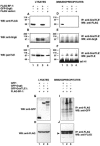
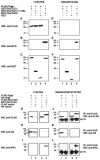
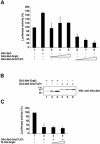
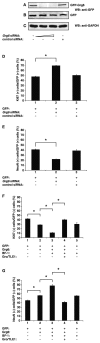
Groucho (Gro)/TLE transcriptional corepressors are involved in a variety of developmental mechanisms, including neuronal differentiation. They contain a conserved C-terminal WD40 repeat domain that mediates interactions with several DNA-binding proteins. In particular, Gro/TLE1 interacts with forkhead transcription factor brain factor 1 (BF-1; also termed FoxG1). BF-1 is an essential regulator of neuronal differentiation during cerebral cortex development and represses transcription together with Gro/TLE1. Gro/TLE-related gene product 6 (Grg6) shares with Gro/TLEs a conserved WD40 repeat domain but is more distantly related at its N-terminal half. We demonstrate that Grg6 is expressed in cortical neural progenitor cells and interacts with BF-1. In contrast to Gro/TLE1, however, Grg6 does not promote, but rather suppresses, BF-1-mediated transcriptional repression. Consistent with these observations, Grg6 interferes with the binding of Gro/TLE1 to BF-1 and does not repress transcription when targeted to DNA. Moreover, coexpression of Grg6 and BF-1 in cortical progenitor cells leads to a decrease in the number of proliferating cells and increased neuronal differentiation. Conversely, Grg6 knockdown by RNA interference causes decreased neurogenesis. These results identify a new role for Grg6 in cortical neuron development and establish a functional link between Grg6 and BF-1.
Figures



References
-
- Bourguignon, C., J. Li, and N. Papalopulu. 1998. XBF-1, a winged helix transcription factor with dual activity, has a role in positioning neurogenesis in Xenopus competent ectoderm. Development 125:4899-4900. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmeier, M. L., M. A. Potok, K. B. Cha, T. Gridley, S. Stifani, J. Meeldijk, H. Clevers, and S. A. Camper. 2003. TCF and Groucho-related genes influence pituitary growth and development. Mol. Endocrinol. 17:2152-2161. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho, L. R., K. S. Woods, B. B. Mendonca, N. Marcal, A. L. Zamparini, S. Stifani, J. M. Brickman, I. V. J. Arnhold, and M. Dattani. 2003. A homozygous mutation in HESX1 is associated with evolving hypopituitarism due to impaired repressor-corepressor interaction. J. Clin. Investig. 112:1192-1201. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, G., and A. J. Courey. 2000. Groucho/TLE family proteins and transcriptional repression. Gene 249:1-16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
