Association of BMI1 with polycomb bodies is dynamic and requires PRC2/EZH2 and the maintenance DNA methyltransferase DNMT1
- PMID: 16314526
- PMCID: PMC1316945
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.11047-11058.2005
Association of BMI1 with polycomb bodies is dynamic and requires PRC2/EZH2 and the maintenance DNA methyltransferase DNMT1
Abstract
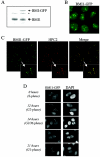
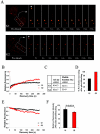
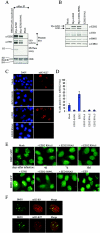
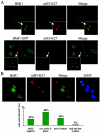
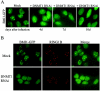
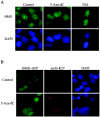
Polycomb group (PcG) proteins are epigenetic chromatin modifiers involved in heritable gene repression. Two main PcG complexes have been characterized. Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) is thought to be involved in the initiation of gene silencing, whereas Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) is implicated in the stable maintenance of gene repression. Here, we investigate the kinetic properties of the binding of one of the PRC1 core components, BMI1, with PcG bodies. PcG bodies are unique nuclear structures located on regions of pericentric heterochromatin, found to be the site of accumulation of PcG complexes in different cell lines. We report the presence of at least two kinetically different pools of BMI1, a highly dynamic and a less dynamic fraction, which may reflect BMI1 pools with different binding capacities to these stable heterochromatin domains. Interestingly, PRC2 members EED and EZH2 appear to be essential for BMI1 recruitment to the PcG bodies. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the maintenance DNA methyltransferase DNMT1 is necessary for proper PcG body assembly independent of DNMT-associated histone deacetylase activity. Together, these results provide new insights in the mechanism for regulation of chromatin silencing by PcG proteins and suggest a highly regulated recruitment of PRC1 to chromatin.
Figures
References
-
- Akasaka, T., M. van Lohuizen, N. van der Lugt, Y. Mizutani-Koseki, M. Kanno, M. Taniguchi, M. Vidal, M. Alkema, A. Berns, and H. Koseki. 2001. Mice doubly deficient for the Polycomb Group genes Mel18 and Bmi1 reveal synergy and requirement for maintenance but not initiation of Hox gene expression. Development 128:1587-1597. - PubMed
-
- Bannister, A. J., R. Schneider, and T. Kouzarides. 2002. Histone methylation: dynamic or static? Cell 109:801-806. - PubMed
-
- Bannister, A. J., P. Zegerman, J. F. Partridge, E. A. Miska, J. O. Thomas, R. C. Allshire, and T. Kouzarides. 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410:120-124. - PubMed
-
- Bruggeman, S. W., M. E. Valk-Lingbeek, P. P. van der Stoop, J. J. Jacobs, K. Kieboom, E. Tanger, D. Hulsman, C. Leung, Y. Arsenijevic, S. Marino, and M. van Lohuizen. 2005. Ink4a and Arf differentially affect cell proliferation and neural stem cell self-renewal in Bmi1-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 19:1438-1443. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
