Allergen-induced peribronchial fibrosis and mucus production mediated by IkappaB kinase beta-dependent genes in airway epithelium
- PMID: 16317067
- PMCID: PMC1308936
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0509235102
Allergen-induced peribronchial fibrosis and mucus production mediated by IkappaB kinase beta-dependent genes in airway epithelium
Abstract
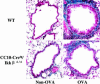
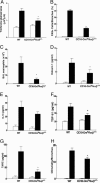
In response to inflammation or injury, airway epithelial cells express inducible genes that may contribute to allergen-induced airway remodeling. To determine the contribution of epithelial cell NF-kappaB activation to the remodeling response, we generated CC10-Cre(tg)/Ikkbeta(delta/delta) mice in which NF-kappaB signaling through IkappaB kinase beta (IKKbeta) is selectively ablated in the airway epithelium by conditional Cre-recombinase expression from the Clara cell (CC10) promoter. Repetitive ovalbumin challenge of mice deficient in airway epithelial IKKbeta prevented nuclear translocation of the RelA NF-kappaB subunit only in airway epithelial cells, resulting in significantly lower peribronchial fibrosis in CC10-Cre(tg)/Ikkbeta(delta/delta) mice compared with littermate controls as assessed by peribronchial trichrome staining and total lung collagen content. Levels of airway mucus, airway eosinophils, and peribronchial CD4+ cells in ovalbumin-challenged mice were also reduced significantly upon airway epithelial Ikkbeta ablation. The diminished inflammatory response was associated with reduced expression of NF-kappaB-regulated chemokines, including eotaxin-1 and thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine, which attract eosinophils and Th2 cells, respectively, into the airway. The number of peribronchial cells expressing TGF-beta1, as well as TGF-beta1 amounts in bronchoalveolar lavage, were also significantly reduced in mice deficient in airway epithelium IKKbeta. Overall, these studies show an important role for NF-kappaB regulated genes in airway epithelium in allergen-induced airway remodeling, including peribronchial fibrosis and mucus production.
Figures

References
-
- Cohn, L., Elias, J. A. & Chupp, G. L. (2004) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22, 789-815. - PubMed
-
- Davies, D. E., Wicks, J., Powell, R. M., Puddicombe, S. M. & Holgate, S. T. (2003) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 111, 215-225. - PubMed
-
- Humbles, A. A., Lloyd, C. M., McMillan, S. J., Friend, D. S., Xanthou, G., McKenna, E. E., Ghiran, S., Gerard, N. P., Yu, C., Orkin, S. H. & Gerard, C. (2004) Science 305, 1776-1779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

