EGF receptor-targeted synthetic double-stranded RNA eliminates glioblastoma, breast cancer, and adenocarcinoma tumors in mice
- PMID: 16318410
- PMCID: PMC1298941
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030006
EGF receptor-targeted synthetic double-stranded RNA eliminates glioblastoma, breast cancer, and adenocarcinoma tumors in mice
Erratum in
- PLoS Med. 2007 Aug;4(8):e266
Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most lethal form of brain cancer. With the available treatments, survival does not exceed 12-14 mo from the time of diagnosis. We describe a novel strategy to selectively induce the death of glioblastoma cells and other cancer cells that over-express the EGF receptor. Using a non-viral delivery vector that homes to the EGF receptor, we target synthetic anti-proliferative dsRNA (polyinosine-cytosine [poly IC]), a strong activator of apoptosis, selectively to cancer cells.
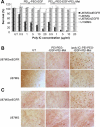
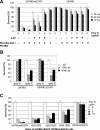
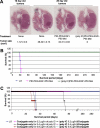
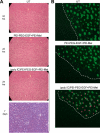
Methods and findings: Poly IC was delivered by means of a non-viral vector: 25kDa polyethylenimine-polyethyleneglycol-EGF (PEI25-PEG-EGF). EGFR-targeted poly IC induced rapid apoptosis in the target cells in vitro and in vivo. Expression of several cytokines and "bystander killing" of untransfected tumor cells was detected in vitro and in vivo. Intra-tumoral delivery of the EGFR-targeted poly IC induced the complete regression of pre-established intracranial tumors in nude mice, with no obvious adverse toxic effects on normal brain tissue. A year after treatment completion the treated mice remain cancer-free and healthy. Similarly, non-viral delivery of poly IC completely eliminated pre-established breast cancer and adenocarcinoma xenografts derived from EGFR over-expressing cancer cell lines, suggesting that the strategy is applicable to other EGFR-over-expressing tumors.
Conclusion: The strategy described has yielded an effective treatment of EGFR over-expressing GBM in an animal model. If this strategy is translated successfully to the clinical setting, it may actually offer help to GBM patients. Moreover the elimination of two additional EGFR over-expressing cancers in vivo suggests that in principle this strategy can be applied to treat other tumors that over-express EGFR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
Glioblastoma multiforme--treating a deadly tumor with both strands of RNA.PLoS Med. 2006 Jan;3(1):e31. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030031. Epub 2005 Dec 6. PLoS Med. 2006. PMID: 16323974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu TF, Tatter SB, Willingham MC, Yang M, Hu JJ, et al. Growth factor receptor expression varies among high-grade gliomas and normal brain: Epidermal growth factor receptor has excellent properties for interstitial fusion protein therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:783–787. - PubMed
-
- Saunders LR, Barber GN. The dsRNA binding protein family: Critical roles, diverse cellular functions. Faseb J. 2003;17:961–983. - PubMed
-
- Chawla-Sarkar M, Lindner DJ, Liu YF, Williams BR, Sen GC, et al. Apoptosis and interferons: Role of interferon-stimulated genes as mediators of apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2003;8:237–249. - PubMed
-
- Parker LM, Fierro-Monti I, Reichman TW, Gunnery S, Mathews MB. Double-stranded RNA-binding proteins and the control of protein synthesis and cell growth. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001;66:485–497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

