A critical role for eukaryotic elongation factor 1A-1 in lipotoxic cell death
- PMID: 16319173
- PMCID: PMC1356587
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0742
A critical role for eukaryotic elongation factor 1A-1 in lipotoxic cell death
Abstract
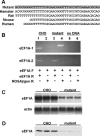
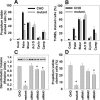
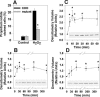
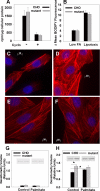
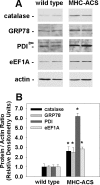
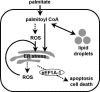
The deleterious consequences of fatty acid (FA) and neutral lipid accumulation in nonadipose tissues, such as the heart, contribute to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. To elucidate mechanisms of FA-induced cell death, or lipotoxicity, we generated Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell mutants resistant to palmitate-induced death and isolated a clone with disruption of eukaryotic elongation factor (eEF) 1A-1. eEF1A-1 involvement in lipotoxicity was confirmed in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts, in which small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown also conferred palmitate resistance. In wild-type CHO and H9c2 cells, palmitate increased reactive oxygen species and induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, changes accompanied by increased eEF1A-1 expression. Disruption of eEF1A-1 expression rendered these cells resistant to hydrogen peroxide- and ER stress-induced death, indicating that eEF1A-1 plays a critical role in the cell death response to these stressors downstream of lipid overload. Disruption of eEF1A-1 also resulted in actin cytoskeleton defects under basal conditions and in response to palmitate, suggesting that eEF1A-1 mediates lipotoxic cell death, secondary to oxidative and ER stress, by regulating cytoskeletal changes critical for this process. Furthermore, our observations of oxidative stress, ER stress, and induction of eEF1A-1 expression in a mouse model of lipotoxic cardiomyopathy implicate this cellular response in the pathophysiology of metabolic disease.
Figures


References
-
- Aasum, E., Belke, D. D., Severson, D. L., Riemersma, R. A., Cooper, M., Andreassen, M., and Larsen, T. S. (2002). Cardiac function and metabolism in Type 2 diabetic mice after treatment with BM 17.0744, a novel PPAR-alpha activator. Am. J. Physiol. 283, H949-H957. - PubMed
-
- Al-Maghrebi, M., Cojocel, C., and Thompson, M. (2004). Regulation of elongation factor-1 mRNA levels by vitamin E in diabetic rat kidneys. FASEB J. 18, C46. - PubMed
-
- Cabrero, A., Alegret, M., Sanchez, R. M., Adzet, T., Laguna, J. C., and Carrera, M. V. (2002). Increased reactive oxygen species production down-regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated alpha pathway in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 10100-10107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

