Hippocampal and parahippocampal volumes in schizophrenia: a structural MRI study
- PMID: 16319377
- PMCID: PMC2632210
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbj030
Hippocampal and parahippocampal volumes in schizophrenia: a structural MRI study
Abstract
Smaller medial temporal lobe volume is a frequent finding in studies of patients with schizophrenia, but the relative contributions of the hippocampus and three surrounding cortical regions (entorhinal cortex, perirhinal cortex, and parahippocampal cortex) are poorly understood. We tested the hypothesis that the volumes of medial temporal lobe regions are selectively changed in schizophrenia. We studied 19 male patients with schizophrenia and 19 age-matched male control subjects. Hippocampal and cortical volumes were estimated using a three-dimensional morphometric protocol for the analysis of high-resolution structural magnetic resonance images, and repeated measures ANOVA was used to test for region-specific differences. Patients had smaller overall medial temporal lobe volumes compared to controls. The volume difference was not specific for either region or hemisphere. The finding of smaller medial temporal lobe volumes in the absence of regional specificity has important implications for studying the functional role of the hippocampus and surrounding cortical regions in schizophrenia.
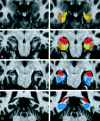
Figures

References
-
- Arnold SE. The medial temporal lobe in schizophrenia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1997;9:460–470. - PubMed
-
- Harrison PJ. The neuropathology of schizophrenia: a critical review of the data and their interpretation. Brain. 1999;122:593–624. - PubMed
-
- Heckers S. Neuroimaging studies of the hippocampus in schizophrenia. Hippocampus. 2001;11:520–528. - PubMed
-
- Nelson MD, Saykin AJ, Flashman LA, Riordan HJ. Hippocampal volume reduction in schizophrenia as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging: a meta-analytic study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55:433–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

