Observation of circulating tumour cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer by real-time fluorescent quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction in peroperative period
- PMID: 16320073
- PMCID: PMC12161055
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-005-0059-3
Observation of circulating tumour cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer by real-time fluorescent quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction in peroperative period
Abstract
Purpose: To assess whether surgical manoeuvre or resection of lung cancer could lead to haematogenous dissemination of malignant cells. In the mean time, the relationship between the sequence of vessel ligation and the haematogenous dissemination of cancer cells during operation was determined.
Methods: Exploiting cytokeratin 19 (CK19)/carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) mRNA as markers, 69 peripheral blood samples were collected from 23 consecutive patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who underwent surgical resection with curative intention in preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative period, respectively. Before the operation, all patients were randomly assigned to one of the two surgical procedure groups according to the order of vessel ligation, PV-first group and PA-first group. Additionally, the ten patients with benign lung disease served as control subjects undergoing surgical resection. The quantity and timing of the shedding of lung cancer cells into the circulation of patients were also monitored by fluorescent quantitative-reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction before, during and after surgery.
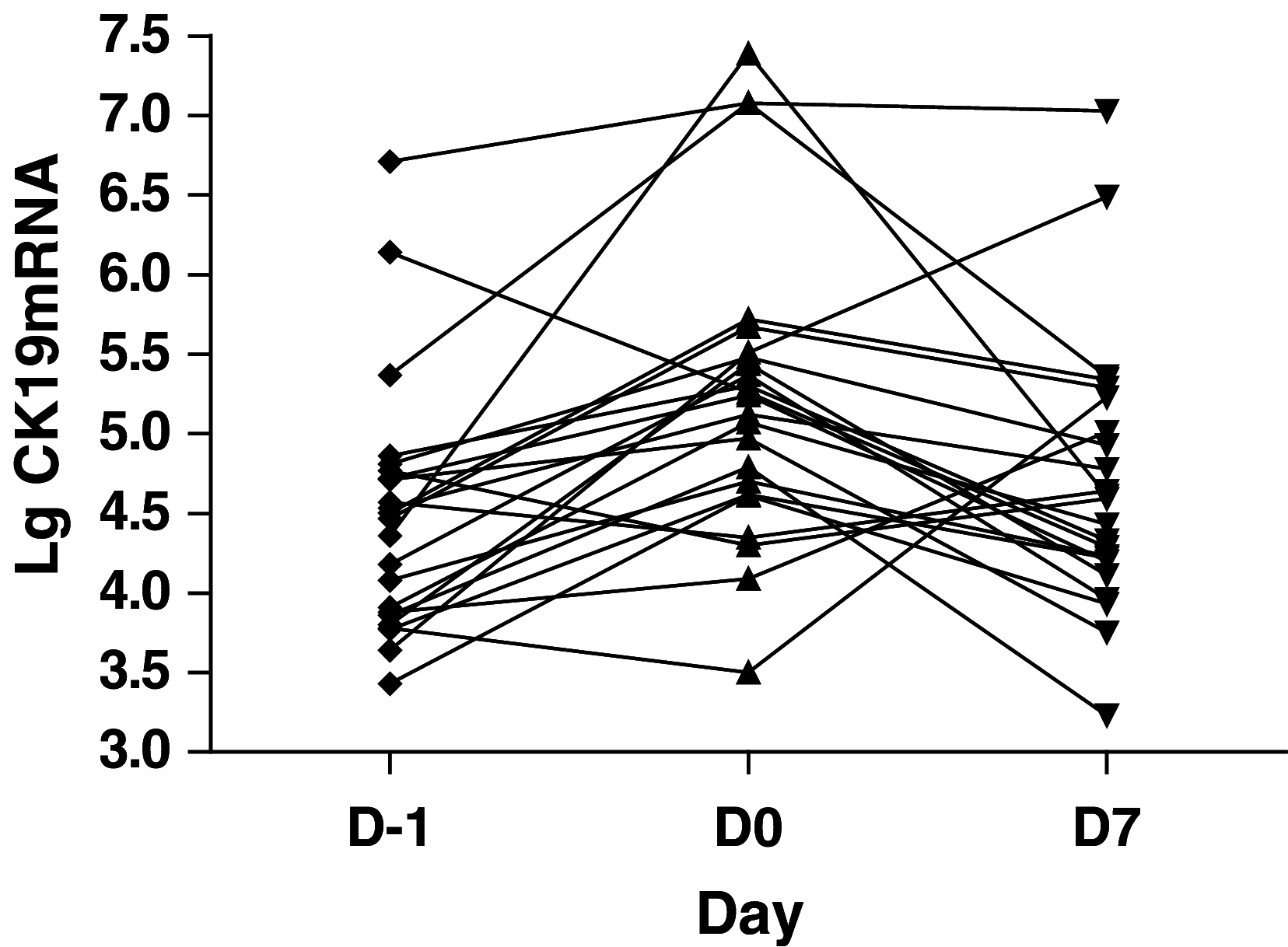
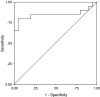
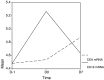
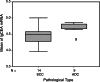
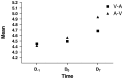
Results: (1) The CK19 diagnostic test: the value of CK19 mRNA in operation was significantly higher than that of preoperation (5.246+/-0.196 vs. 4.472+/-0.164, P=0.000) and postoperation (5.246+/-0.196 vs. 4.694+/-0.177, P=0.013). The values between adenocarcinoma and squamous carcinoma were strikingly different (4.9110+/-1.0315 vs. 4.1891+/-0.4126, t=2.364, P=0.028). The values between PV-first group and PA-first group during perioperative period appear to be different (4.503 vs. 5.085, P=0.086). Before operation, of the 23 cases studied, 14 cases were positive (60.9%). Surprisingly, circulating epithelial cells were detected in two patients resected for benign lung disease. (2) The CEA diagnostic test: the level of CEA mRNA ascended continuously within this period. The postoperative values were significantly higher than those of preoperation (4.874 vs. 4.483, P=0.000) and those of operative day (4.874 vs. 4.537, P=0.000). The values between PV-first group and PA-first group appear to reach statistical significance (4.397 vs. 4.817, P=0.075). At the same time, there was a correlation between preoperative T-stage and perioperative CEA mRNA (4.267 vs. 4.760, P=0.025). Among the 23 cases, 10 cases were positive (43.5%). Both patients with benign lung disease served as control subjects undergoing surgical resection and the volunteers were negative.
Conclusions: A considerable proportion of patients who appear to have resectable NSCLC might be regarded as having systemic disease, which is often undetectable by current tumour staging method. In terms of a marker used for the NSCLC patients who undergo operation, CEA is more suitable than CK19. The CK19-expressing epithelial cells are released intraoperatively into the circulation, meanwhile CEA-expressing tumour cells are disseminated mostly postoperatively. Surgical manipulation could promote the release of tumour cells into the bloodstream, but the ligation of pulmonary vein before the ligation of the pulmonary artery may partly prevent such release during surgery.
Figures


References
-
- Bockmann B, Grill HJ, Giesing M (2001) Molecular characterization of minimal residual cancer cells in patients with solid tumors. Biomol Eng 17(3):95–111 - PubMed
-
- Castaldo G, Tomaiuolo R, Sanduzzi A, Bocchino ML, Ponticiello A, Barra E, Vitale D, Bariffi F, Sacchetti L, Salvatore F (1997) Lung cancer metastatic cells detected in blood by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and dot-blot analysis. J Clin Oncol 15(11):3388–3393 - PubMed
-
- Curry BJ, Myers K, Hersey P (1999) MART-1 is expressed less frequently on circulating melanoma cells in patients who develop distant compared with locoregional metastases. J Clin Oncol 17(8):2562–2571 - PubMed
-
- Fidler IJ (1991) The biology of human cancer metastasis. Acta Oncol 30(6):668–675 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

