The oxygen sensing signal cascade under the influence of reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 16321790
- PMCID: PMC1569600
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1760
The oxygen sensing signal cascade under the influence of reactive oxygen species
Abstract
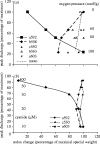
Structural and functional integrity of organ function profoundly depends on a regular oxygen and glucose supply. Any disturbance of this supply becomes life threatening and may result in severe loss of organ function. Particular reductions in oxygen availability (hypoxia) caused by respiratory or blood circulation irregularities cannot be tolerated for longer periods due to an insufficient energy supply by anaerobic glycolysis. Complex cellular oxygen sensing systems have evolved to tightly regulate oxygen homeostasis. In response to variations in oxygen partial pressure (PO2), these systems induce adaptive and protective mechanisms to avoid or at least minimize tissue damage. These various responses might be based on a range of oxygen sensing signal cascades including an isoform of the neutrophil NADPH oxidase, different electron carrier units of the mitochondrial chain such as a specialized mitochondrial, low PO2 affinity cytochrome c oxidase (aa3) and a subfamily of 2-oxoglutarate dependent dioxygenases termed HIF (hypoxia inducible factor) prolyl-hydroxylase and HIF asparaginyl hydroxylase called factor-inhibiting HIF (FIH-1). Thus, specific oxygen sensing cascades involving reactive oxygen species as second messengers may by means of their different oxygen sensitivities, cell-specific and subcellular localization help to tailor various adaptive responses according to differences in tissue oxygen availability.
Figures


References
-
- Acker T, Acker H. Cellular oxygen sensing need in CNS function: physiological and pathological implications [Review] J. Exp. Biol. 2004;207:3171–3188. 10.1242/jeb.01075 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Acker H, Lübbers D.W. The kinetics of local tissue PO2 decrease after perfusion stop within the carotid body of the cat in vivo and in vitro. Pflüg. Arch. 1977;369:135–140. 10.1007/BF00591569 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Acker H, Lübbers D.W, Purves M.J, Tan E.D. Measurements of the partial pressure of oxygen in the carotid body of fetal sheep and newborn lambs. J. Dev. Physiol. 1980;2:323–328. - PubMed
-
- Archer S.L, Reeve H.L, Michelakis E, Puttagunta L, Waite R, Nelson D.P, Dinauer M.C, Weir E.K. O2 sensing is preserved in mice lacking the gp91 phox subunit of NADPH oxidase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1999;96:7944–7949. 10.1073/pnas.96.14.7944 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arthur P.G, Ngo C.T, Moretta P, Guppy M. Lack of oxygen sensing by mitochondria in platelets. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999;266:215–219. 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00846.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

