Dual oxidases
- PMID: 16321800
- PMCID: PMC1569583
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1767
Dual oxidases
Abstract
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have an important role in various physiological processes including host defence, mitogenesis, hormone biosynthesis, apoptosis and fertilization. Currently, the most characterized ROS-producing system operates in phagocytic cells, where ROS generated during phagocytosis act in host defence. Recently, several novel homologues of the phagocytic oxidase have been discovered and this protein family is now designated as the NOX/DUOX family of NADPH oxidases. NOX/DUOX enzymes function in a variety of tissues, including colon, kidney, thyroid gland, testis, salivary glands, airways and lymphoid organs. Importantly, members of the enzyme family are also found in non-mammalian species, including Caenorhabditis elegans and sea urchin. The physiological functions of novel NADPH oxidase enzymes are currently largely unknown. This review focuses on our current knowledge about dual oxidases.
Figures


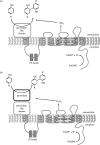
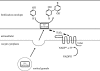

References
-
- Ambasta R.K, Kumar P, Griendling K.K, Schmidt H.H, Busse R, Brandes R.P. Direct interaction of the novel Nox proteins with p22phox is required for the formation of a functionally active NADPH oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:45 935–45 941. 10.1074/jbc.M406486200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bokoch G.M, Knaus U.G. NADPH oxidases: not just for leukocytes anymore! Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003;28:502–508. 10.1016/S0968-0004(03)00194-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Deken X, Wang D, Many M.C, Costagliola S, Libert F, Vassart G, Dumont J.E, Miot F. Cloning of two human thyroid cDNAs encoding new members of the NADPH oxidase family. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:23 227–23 233. 10.1074/jbc.M000916200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Deken X, Wang D, Dumont J.E, Miot F. Characterization of ThOX proteins as components of the thyroid H(2)O(2)-generating system. Exp. Cell Res. 2002;273:187–196. 10.1006/excr.2001.5444 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dupuy C, Deme D, Kaniewski J, Pommier J, Virion A. Ca2+ regulation of thyroid NADPH-dependent H2O2 generation. FEBS Lett. 1988;233:74–78. 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81358-9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
