Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase: a target and generator of oxidative stress
- PMID: 16321804
- PMCID: PMC1569585
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1764
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase: a target and generator of oxidative stress
Abstract
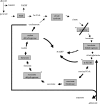
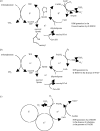
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (alpha-KGDH) is a highly regulated enzyme, which could determine the metabolic flux through the Krebs cycle. It catalyses the conversion of alpha-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA and produces NADH directly providing electrons for the respiratory chain. alpha-KGDH is sensitive to reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibition of this enzyme could be critical in the metabolic deficiency induced by oxidative stress. Aconitase in the Krebs cycle is more vulnerable than alpha-KGDH to ROS but as long as alpha-KGDH is functional NADH generation in the Krebs cycle is maintained. NADH supply to the respiratory chain is limited only when alpha-KGDH is also inhibited by ROS. In addition being a key target, alpha-KGDH is able to generate ROS during its catalytic function, which is regulated by the NADH/NAD+ ratio. The pathological relevance of these two features of alpha-KGDH is discussed in this review, particularly in relation to neurodegeneration, as an impaired function of this enzyme has been found to be characteristic for several neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Generation of reactive oxygen species in the reaction catalyzed by alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.J Neurosci. 2004 Sep 8;24(36):7771-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1842-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15356188 Free PMC article.
-
Production of reactive oxygen species in brain mitochondria: contribution by electron transport chain and non-electron transport chain sources.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005 Sep-Oct;7(9-10):1140-9. doi: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.1140. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005. PMID: 16115017 Review.
-
Inhibition of Krebs cycle enzymes by hydrogen peroxide: A key role of [alpha]-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in limiting NADH production under oxidative stress.J Neurosci. 2000 Dec 15;20(24):8972-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-24-08972.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11124972 Free PMC article.
-
Selective NADH communication from α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase to mitochondrial transhydrogenase prevents reactive oxygen species formation under reducing conditions in the heart.Basic Res Cardiol. 2020 Aug 3;115(5):53. doi: 10.1007/s00395-020-0815-1. Basic Res Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32748289 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mitochondrial dehydrogenases in the generation of oxidative stress.Neurochem Int. 2013 Apr;62(5):757-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.01.012. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Neurochem Int. 2013. PMID: 23357482 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucose Metabolic Characterization of Human Aqueous Humor in Relation to Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Mar 9;61(3):49. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.3.49. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32232346 Free PMC article.
-
Proinflammatory cytokines differentially regulate adipocyte mitochondrial metabolism, oxidative stress, and dynamics.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 May 1;306(9):E1033-45. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00422.2013. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24595304 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic profiling of mitochondria: what does it tell us about the ageing brain?Aging (Albany NY). 2016 Dec 13;8(12):3161-3179. doi: 10.18632/aging.101131. Aging (Albany NY). 2016. PMID: 27992860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Essential Role of Mitochondrial α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase E2 in the Basal Immune Response Against Bacterial Pathogens in Tomato.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Oct 30;11:579772. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.579772. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33193523 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Mg2+ Intake and the Na+/Mg2+ Exchanger SLC41A1 Influence Components of Mitochondrial Energetics in Murine Cardiomyocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 3;21(21):8221. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218221. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33153064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrosio G, Zweier J.L, Flaherty J.T. The relationship between oxygen radical generation and impairment of myocardial energy metabolism following post-ischemic reperfusion. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1991;23:1359–1374. 10.1016/0022-2828(91)90183-M - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ambrosio G, et al. Evidence that mitochondrial respiration is a source of potentially toxic oxygen free radicals in intact rabbit hearts subjected to ischemia and reflow. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:18 532–18 541. - PubMed
-
- Andersson U, Leighton B, Young M.E, Blomstrand E, Newsholme E.A. Inactivation of aconitase and oxoglutarate dehydrogenase in skeletal muscle in vitro by superoxide anions and/or nitric oxide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998;249:512–516. 10.1006/bbrc.1998.9171 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ballou D, Palmer G, Massey V. Direct demonstration of superoxide anion production during the oxidation of reduced flavin and of its catalytic decomposition by erythrocuprein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1969;36:898–904. 10.1016/0006-291X(69)90288-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bando Y, Aki K. Mechanisms of generation of oxygen radicals and reductive mobilization of ferritin iron by lipoamide dehydrogenase. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 1991;109:450–454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

