Cell-penetrating peptide conjugates of peptide nucleic acids (PNA) as inhibitors of HIV-1 Tat-dependent trans-activation in cells
- PMID: 16321967
- PMCID: PMC1301599
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki991
Cell-penetrating peptide conjugates of peptide nucleic acids (PNA) as inhibitors of HIV-1 Tat-dependent trans-activation in cells
Abstract
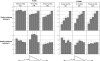
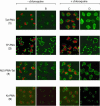
The trans-activation response (TAR) RNA stem-loop that occurs at the 5' end of HIV RNA transcripts is an important antiviral target and is the site of interaction of the HIV-1 Tat protein together with host cellular factors. Oligonucleotides and their analogues targeted to TAR are potential antiviral candidates. We have investigated a range of cell penetrating peptide (CPP) conjugates of a 16mer peptide nucleic acid (PNA) analogue targeted to the apical stem-loop of TAR and show that disulfide-linked PNA conjugates of two types of CPP (Transportan or a novel chimeric peptide R6-Penetratin) exhibit dose-dependent inhibition of Tat-dependent trans-activation in a HeLa cell assay when incubated for 24 h. Activity is reached within 6 h if the lysosomotropic reagent chloroquine is co-administered. Fluorescein-labelled stably-linked conjugates of Tat, Transportan or Transportan TP10 with PNA were inactive when delivered alone, but attained trans-activation inhibition in the presence of chloroquine. Confocal microscopy showed that such fluorescently labelled CPP-PNA conjugates were sequestered in endosomal or membrane-bound compartments of HeLa cells, which varied in appearance depending on the CPP type. Co-administration of chloroquine was seen in some cases to release fluorescence from such compartments into the nucleus, but with different patterns depending on the CPP. The results show that CPP-PNA conjugates of different types can inhibit Tat-dependent trans-activation in HeLa cells and have potential for development as antiviral agents. Endosomal or membrane release is a major factor limiting nuclear delivery and trans-activation inhibition.
Figures




References
-
- Bennett C.F., Chiang M.-Y., Chan H., Shoemaker J.E.E., Mirabelli C.K. Cationic lipids enhance cellular uptake and activity of phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992;41:1023–1033. - PubMed
-
- Egholm M., Buchardt O., Christensen L., Behrens C., Freier S.M., Driver D.A., Berg R.H., Kim S.K., Norden B., Nielsen P. PNA hybridizes to complementary oligonucleotides obeying the Watson–Crick hydrogen bonding rules. Nature. 1993;365:566–568. - PubMed
-
- Summerton J., Stein D., Huang S.B., Matthews P., Weller D.D., Partridge M. Morpholino and phosphorothioate antisense oligomers compared in cell-free and in cell systems. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1997;7:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Koppelhus U., Awasthi S.K., Zachar V., Holst H.U., Ebbeson P., Nielsen P.E. Cell-dependent differential cellular uptake of PNA, peptides and PNA–peptide conjugates. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 2002;12:51–63. - PubMed
-
- Lochmann D., Jauk E., Zimmer A. Drug delivery of oligonucleotides by peptides. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004;58:237–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

