Chromosomal fragmentation is the major consequence of the rdgB defect in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 16322510
- PMCID: PMC1456232
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.051144
Chromosomal fragmentation is the major consequence of the rdgB defect in Escherichia coli
Abstract
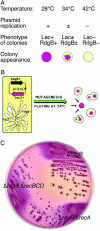
The rdgB mutants depend on recombinational repair of double-strand breaks. To assess other consequences of rdgB inactivation in Escherichia coli, we isolated RdgB-dependent mutants. All transposon inserts making cells dependent on RdgB inactivate genes of double-strand break repair, indicating that chromosomal fragmentation is the major consequence of RdgB inactivation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chromosomal fragmentation in dUTPase-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli and its recombinational repair.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Mar;51(5):1279-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2003.03924.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 14982624
-
RecA-dependent mutants in Escherichia coli reveal strategies to avoid chromosomal fragmentation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Nov 16;101(46):16262-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405943101. Epub 2004 Nov 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15531636 Free PMC article.
-
RdgB acts to avoid chromosome fragmentation in Escherichia coli.Mol Microbiol. 2003 Jun;48(6):1711-25. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03540.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12791149
-
Repair of methyl lesions in DNA and RNA by oxidative demethylation.Neuroscience. 2007 Apr 14;145(4):1222-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.11.018. Epub 2006 Dec 18. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17175108 Review.
-
A cut above: discovery of an alternative excision repair pathway in bacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 5;99(5):2581-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.062062599. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11880612 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Comment on "A commensal strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis protects against skin neoplasia" by Nakatsuji et al.Sci Adv. 2019 Sep 11;5(9):eaaw3915. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw3915. eCollection 2019 Sep. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31535021 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous Recombination-Experimental Systems, Analysis, and Significance.EcoSal Plus. 2011 Dec;4(2):10.1128/ecosalplus.7.2.6. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.7.2.6. EcoSal Plus. 2011. PMID: 26442506 Free PMC article.
-
Genomewide phenotypic analysis of growth, cell morphogenesis, and cell cycle events in Escherichia coli.Mol Syst Biol. 2018 Jun 25;14(6):e7573. doi: 10.15252/msb.20177573. Mol Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29941428 Free PMC article.
-
Pivotal role of inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase in maintaining genome stability and the prevention of apoptosis in human cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032313. Epub 2012 Feb 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384212 Free PMC article.
-
Production of clastogenic DNA precursors by the nucleotide metabolism in Escherichia coli.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jan;75(1):230-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06994.x. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19943897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bessman, M. J., D. N. Frick and S. F. O'Handley, 1996. The MutT proteins or “Nudix” hydrolases, a family of versatile, widely distributed, “housecleaning” enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 25059–25062. - PubMed
-
- Bradshaw, J. S., and A. Kuzminov, 2003. RdgB acts to avoid chromosome fragmentation in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 48: 1711–1725. - PubMed
-
- Chung, J. H., H. Y. Park, J. H. Lee and Y. Jang, 2002. Identification of the dITP- and XTP-hydrolyzing protein from Escherichia coli. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 35: 403–408. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

