zds1, a novel gene encoding an ortholog of Zds1 and Zds2, controls sexual differentiation, cell wall integrity and cell morphology in fission yeast
- PMID: 16322512
- PMCID: PMC1456246
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.050906
zds1, a novel gene encoding an ortholog of Zds1 and Zds2, controls sexual differentiation, cell wall integrity and cell morphology in fission yeast
Abstract
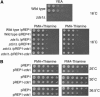
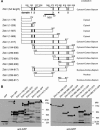
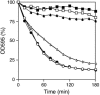
While screening for genes that reverse the sporulation-deficient phenotype of the ras1delta diploid Schizosaccharomyces pombe strain, we identified zds1. This gene shares sequence homology with the ZDS1 and ZDS2 genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which appear to be involved in multiple cellular events. Expression of Zds1 in ras1delta diploid cells elevated their sporulation rate from 0.3 to 11.2%. Expression of the Zds1 C-terminal region increased the sporulation rate further (to 21.9%) while introduction of the Zds1 N-terminal region had no effect. zds1 expression did not induce sporulation in strains with mutations in genes participating in the downstream MAP kinase cascade. The zds1-disrupted strain is sensitive to CaCl2, and this effect is suppressed by the C-terminal region of Zds1. The growth of the zds1delta strain is markedly inhibited by cold temperatures, while its viability decreased in the stationary phase. Moreover, the zds1delta strain is round in shape and very sensitive to zymolyase, and its cell wall becomes thicker than that of wild type. Thus, zds1 must be required to maintain cell wall integrity. The Zds1-GFP fusion protein localized to the cytosol, the septum, and the cell cortex. Its localization in the septum was dependent on its C-terminal region. Overexpression of the C-terminal region of Zds1 induced multi-septa and abnormal zygotes. We propose that the C-terminal region is the functional domain of Zds1 while the N-terminal region is a negative regulatory region. Thus, Zds1 is involved in multiple cellular events in fission yeast, including sexual differentiation, Ca2+ tolerance, cell wall integrity, viability in the stationary phase, and cell morphology.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The beta-1,3-glucanosyltransferase gas4p is essential for ascospore wall maturation and spore viability in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Jun;68(5):1283-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06233.x. Epub 2008 Apr 8. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18410286
-
Fission yeast Rho5p GTPase is a functional paralogue of Rho1p that plays a role in survival of spores and stationary-phase cells.Eukaryot Cell. 2006 Mar;5(3):435-46. doi: 10.1128/EC.5.3.435-446.2006. Eukaryot Cell. 2006. PMID: 16524899 Free PMC article.
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae YCRO17c/CWH43 encodes a putative sensor/transporter protein upstream of the BCK2 branch of the PKC1-dependent cell wall integrity pathway.Yeast. 2001 Jun 30;18(9):827-40. doi: 10.1002/yea.731. Yeast. 2001. PMID: 11427965
-
Splitting of the fission yeast septum.FEMS Yeast Res. 2007 Sep;7(6):761-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2007.00266.x. Epub 2007 Jun 27. FEMS Yeast Res. 2007. PMID: 17596184 Review.
-
Cdc42 regulates polarized growth and cell integrity in fission yeast.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Feb;42(1):201-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20130155. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 24450652 Review.
Cited by
-
A dominant negative 14-3-3 mutant in Schizosaccharomyces pombe distinguishes the binding proteins involved in sexual differentiation and check point.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 3;18(10):e0291524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291524. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37788281 Free PMC article.
-
Zds1 regulates PP2A(Cdc55) activity and Cdc14 activation during mitotic exit through its Zds_C motif.J Cell Sci. 2012 Jun 15;125(Pt 12):2875-84. doi: 10.1242/jcs.097865. Epub 2012 Mar 16. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22427694 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and role of an RNA-binding protein Msa2 in controlling the sexual differentiation of fission yeast.Curr Genet. 2011 Jun;57(3):191-200. doi: 10.1007/s00294-011-0335-5. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Curr Genet. 2011. PMID: 21409593
-
Comparative genetic analysis of PP2A-Cdc55 regulators in budding yeast.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(13):2073-83. doi: 10.4161/cc.29064. Epub 2014 May 6. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24800822 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle checkpoint regulators reach a zillion.Cell Cycle. 2013 May 15;12(10):1501-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.24637. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23598718 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alfa, C., P. Fantes, J. Hyams, M. McLeod and E. Warbrick, 1993. Experiments With Fission Yeast: A Laboratory Course Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
-
- Bandhakavi, S., R. O. McCann, D. E. Hanna and C. V. Glover, 2003. Genetic interactions among ZDS1,2, CDC37, and protein kinase CK2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 554: 295–300. - PubMed
-
- Basi, G., E. K. Schmid and Maundrell, 1993. TATA box mutations in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe nmt1 promoter affect transcription efficiency but not the transcription start point or thiamine repressibility. Gene 123: 131–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

