A simple electrostatic switch important in the activation of type I protein kinase A by cyclic AMP
- PMID: 16322564
- PMCID: PMC2242374
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.051723606
A simple electrostatic switch important in the activation of type I protein kinase A by cyclic AMP
Abstract
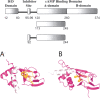
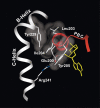
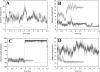
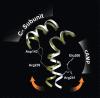
Cyclic AMP activates protein kinase A by binding to an inhibitory regulatory (R) subunit and releasing inhibition of the catalytic (C) subunit. Even though crystal structures of regulatory and catalytic subunits have been solved, the precise molecular mechanism by which cyclic AMP activates the kinase remains unknown. The dynamic properties of the cAMP binding domain in the absence of cAMP or C-subunit are also unknown. Here we report molecular-dynamics simulations and mutational studies of the RIalpha R-subunit that identify the C-helix as a highly dynamic switch which relays cAMP binding to the helical C-subunit binding regions. Furthermore, we identify an important salt bridge which links cAMP binding directly to the C-helix that is necessary for normal activation. Additional mutations show that a hydrophobic "hinge" region is not as critical for the cross-talk in PKA as it is in the homologous EPAC protein, illustrating how cAMP can control diverse functions using the evolutionarily conserved cAMP-binding domains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crystal structures of RIalpha subunit of cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase complexed with (Rp)-adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphothioate and (Sp)-adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphothioate, the phosphothioate analogues of cAMP.Biochemistry. 2004 Jun 1;43(21):6620-9. doi: 10.1021/bi0302503. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15157095
-
Dynamic binding of PKA regulatory subunit RI alpha.Structure. 2006 Jan;14(1):141-9. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2005.09.019. Structure. 2006. PMID: 16407073
-
Definition of an electrostatic relay switch critical for the cAMP-dependent activation of protein kinase A as revealed by the D170A mutant of RIalpha.Proteins. 2007 Oct 1;69(1):112-24. doi: 10.1002/prot.21446. Proteins. 2007. PMID: 17596845
-
Epac proteins: multi-purpose cAMP targets.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Dec;31(12):680-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.10.002. Epub 2006 Nov 2. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 17084085 Review.
-
Dynamics of signaling by PKA.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Dec 30;1754(1-2):25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.08.024. Epub 2005 Sep 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 16214430 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclic AMP- and (Rp)-cAMPS-induced conformational changes in a complex of the catalytic and regulatory (RI{alpha}) subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010 Oct;9(10):2225-37. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900388-MCP200. Epub 2010 Feb 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20167947 Free PMC article.
-
An electrostatic network and long-range regulation of Src kinases.Protein Sci. 2008 Nov;17(11):1871-80. doi: 10.1110/ps.037457.108. Epub 2008 Aug 7. Protein Sci. 2008. PMID: 18687871 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and rearrangements in the carboxy-terminal region of SpIH channels.Structure. 2007 Jun;15(6):671-82. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.04.008. Structure. 2007. PMID: 17562314 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the cAMP-inducible allosteric switch in protein kinase A RIalpha.Protein Sci. 2010 Jun;19(6):1213-21. doi: 10.1002/pro.400. Protein Sci. 2010. PMID: 20512974 Free PMC article.
-
Electrostatic changes in phosphorylase kinase induced by its obligatory allosteric activator Ca2+.Protein Sci. 2007 Mar;16(3):517-27. doi: 10.1110/ps.062577507. Protein Sci. 2007. PMID: 17322534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antoni, F.A. 2000. Molecular diversity of cyclic AMP signalling. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 21: 103–132. - PubMed
-
- Berendsen, H.J.C., Postma, J.P.M., van Gunsteren, W.F., DiNola, A., and Haak, J.R. 1984. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 81: 3684–3690.
-
- Brooks, B.R., Bruccoleri, R.E., Olafson, B.D., States, D.J., Swaminathan, S., and Karplus, M. 1983. CHARMM–A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 4: 187–217.
-
- Bubis, J., Neitzel, J.J., Saraswat, L.D., and Taylor, S.S. 1988. A point mutation abolishes binding of cAMP to site A in the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 9668–9673. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

