Solid-state NMR studies of a diverged microsomal amino-proximate delta12 desaturase peptide reveal causes of stability in bilayer: tyrosine anchoring and arginine snorkeling
- PMID: 16326900
- PMCID: PMC1367276
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.105.067884
Solid-state NMR studies of a diverged microsomal amino-proximate delta12 desaturase peptide reveal causes of stability in bilayer: tyrosine anchoring and arginine snorkeling
Abstract
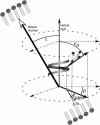
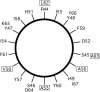
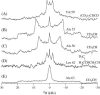
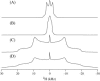
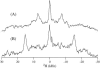
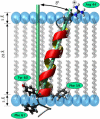
This study reports the solid-state NMR spectroscopic characterization of the amino-proximate transmembrane domain (TM-A) of a diverged microsomal delta12-desaturase (CREP-1) in a phospholipid bilayer. A series of TM-A peptides were synthesized with 2H-labeled side chains (Ala-53, -56, and -63, Leu-62, Val-50), and their dynamic properties were studied in 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (DMPC) bilayers at various temperatures. At 6 mol % peptide to lipid, 31P NMR spectra indicated that the peptides did not significantly disrupt the phospholipid bilayer in the L(alpha) phase. The 2H NMR spectra from Ala-53 and Ala-56 samples revealed broad Pake patterns with quadrupolar splittings of 16.9 kHz and 13.3 kHz, respectively, indicating restricted motion confined within the hydrocarbon core of the phospholipid bilayer. Conversely, the deuterated Ala-63 sample revealed a peak centered at 0 kHz with a linewidth of 1.9 kHz, indicating increased side-chain motion and solvent exposure relative to the spectra of the other Ala residues. Val-50 and Leu-62 showed Pake patterns, with quadrupolar splittings of 3.5 kHz and 3.7 kHz, respectively, intermediate to Ala-53/Ala-56 and Ala-63. This indicates partial motional averaging and supports a model with the Val and Leu residues embedded inside the lipid bilayer. Solid-state NMR spectroscopy performed on the 2H-labeled Ala-56 TM-A peptide incorporated into magnetically aligned phospholipid bilayers indicated that the peptide is tilted 8 degrees with respect to the membrane normal of the lipid bilayer. Snorkeling and anchoring interactions of Arg-44 and Tyr-60, respectively, with the polar region or polar hydrophobic interface of the lipid bilayer are suggested as control elements for insertional depth and orientation of the helix in the lipid matrix. Thus, this study defines the location of key residues in TM-A with respect to the lipid bilayer, describes the conformation of TM-A in a biomembrane mimic, presents a peptide-bilayer model useful in the consideration of local protein folding in the microsomal desaturases, and presents a model of arginine and tyrosine control of transmembrane protein stability and insertion.
Figures
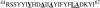
Similar articles
-
Investigating the dynamic properties of the transmembrane segment of phospholamban incorporated into phospholipid bilayers utilizing 2H and 15N solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Biochemistry. 2004 Nov 9;43(44):13899-909. doi: 10.1021/bi0490993. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15518538
-
Solid-state NMR spectroscopic studies of an integral membrane protein inserted into aligned phospholipid bilayer nanotube arrays.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Aug 11;126(31):9504-5. doi: 10.1021/ja047317+. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 15291530
-
Influence of Lipid Saturation, Hydrophobic Length and Cholesterol on Double-Arginine-Containing Helical Peptides in Bilayer Membranes.Chembiochem. 2019 Nov 4;20(21):2784-2792. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201900282. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Chembiochem. 2019. PMID: 31150136 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and mechanism of beta-hairpin antimicrobial peptides in lipid bilayers from solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Mol Biosyst. 2009 Apr;5(4):317-22. doi: 10.1039/b820398a. Epub 2009 Jan 27. Mol Biosyst. 2009. PMID: 19396367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid bilayers: an essential environment for the understanding of membrane proteins.Magn Reson Chem. 2007 Dec;45 Suppl 1:S2-11. doi: 10.1002/mrc.2077. Epub 2007 Dec 19. Magn Reson Chem. 2007. PMID: 18095258 Review.
Cited by
-
Atypical biosynthetic properties of a Delta 12/nu+3 desaturase from the model basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Feb;75(4):1156-64. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02049-08. Epub 2008 Dec 16. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19088315 Free PMC article.
-
Charged or aromatic anchor residue dependence of transmembrane peptide tilt.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 8;285(41):31723-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.152470. Epub 2010 Jul 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20667827 Free PMC article.
-
Side chain and backbone dynamics of phospholamban in phospholipid bilayers utilizing 2H and 15N solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Biochemistry. 2007 Oct 23;46(42):11695-706. doi: 10.1021/bi700749q. Epub 2007 Oct 2. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17910421 Free PMC article.
-
The membrane activity of the antimicrobial peptide caerin 1.1 is pH dependent.Biophys J. 2023 Mar 21;122(6):1058-1067. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.01.021. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 36680343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cook, H. W. 1991. Fatty acid desaturation and chain elongation in eukaryotes. In Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes. D. E. Vance and J. Vance, editors. Elsevier, New York. 141–169.
-
- Singer, S. J. 1974. Molecular organization of membranes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 43:805–833. - PubMed
-
- Broun, P., J. Shanklin, E. Whittle, and C. Sommerville. 1998. Catalytic plasticity of fatty acid modification enzymes underlying chemical diversity of plant lipids. Science. 282:1315–1317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

