Association of housing disrepair indicators with cockroach and rodent infestations in a cohort of pregnant Latina women and their children
- PMID: 16330367
- PMCID: PMC1314924
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.7588
Association of housing disrepair indicators with cockroach and rodent infestations in a cohort of pregnant Latina women and their children
Abstract
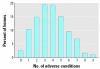
Health burdens associated with poor housing and indoor pest infestations are likely to affect young children in particular, who spend most of their time indoors at home. We completed environmental assessments in 644 homes of pregnant Latina women and their children living in the Salinas Valley, California. High residential densities were common, with 39% of homes housing > 1.5 persons per room. Housing disrepair was also common: 58% of homes had peeling paint, 43% had mold, 25% had water damage, and 11% had rotting wood. Evidence of cockroaches and rodents was present in 60% and 32% of homes, respectively. Compared with representative national survey data from the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, homes in our sample were more likely to have rodents, peeling paint, leaks under sinks, and much higher residential densities. The odds of rodent infestations in homes increased in the presence of peeling paint [odds ratio (OR) 2.1; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.5-3.1], water damage (OR 1.9; 95% CI, 1.2-2.7), and mold (OR 1.5; 95% CI, 1.0-2.1). The odds of cockroach infestation increased in the presence of peeling paint (OR 3.8; 95% CI, 2.7-5.6), water damage (OR 1.9; 95% CI, 1.2-2.9), or high residential density (OR 2.1; 95% CI, 1.2-3.8). Homes that were less clean than average were more prone to both types of infestations. Pesticides were stored or used in 51% of households, partly to control roach and rodent infestations. These data indicate that adverse housing conditions are common in this community and increase the likelihood of pest infestations and home pesticide use. Interventions to improve housing and promote children's health and safety in this population are needed.
Figures
References
-
- Applied Survey Research and the Center for Community Advocacy 2001. Farmworker Housing and Health Needs Assessment Study of the Salinas and Pajaro Valleys Final Report. Salinas, CA:Applied Survey Research and the Center for Community Advocacy.
-
- Baumholtz MA, Parish LC, Witkowski JA, Nutting WB. The medical importance of cockroaches. Int J Dermatol. 1997;36:90–96. - PubMed
-
- Bornehag CG, Blomquist G, Gyntelberg F, Jarvholm B, Malmberg P, Nordvall L, et al. Dampness in buildings and health. Nordic interdisciplinary review of the scientific evidence on associations between exposure to “dampness” in buildings and health effects (NORDDAMP) Indoor Air. 2001;11(2):72–86. - PubMed
-
- Bornehag CG, Sundell J, Sigsgaard T. Dampness in buildings and health (DBH): Report from an ongoing epidemiological investigation on the association between indoor environmental factors and health effects among children in Sweden. Indoor Air. 2004;14(suppl 7):59–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources