Organophosphate urinary metabolite levels during pregnancy and after delivery in women living in an agricultural community
- PMID: 16330368
- PMCID: PMC1314925
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.7894
Organophosphate urinary metabolite levels during pregnancy and after delivery in women living in an agricultural community
Abstract
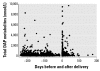
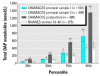
Little information has been published about pesticide exposures experienced by pregnant women. We measured six dialkyl phosphate (DAP) urinary metabolites of organophosphate (OP) pesticides in 600 pregnant, low-income women living in the Salinas Valley, California, an agricultural area. A total of 28% were employed as farm fieldworkers during pregnancy, and 81% had at least one household member who worked in agriculture. Samples were collected twice during pregnancy (mean = 13 and 26 weeks' gestation, respectively) and just after delivery (mean = 9 days). As in other studies, dimethyldithiophosphate levels were higher than those of other urinary OP metabolites. Total DAP metabolite levels in samples collected after delivery were higher than in samples collected during pregnancy. Median metabolite levels at the first and second prenatal sampling points and at the postpartum collection were 102.8, 106.8, and 227.2 nmol/L, respectively. Both prenatal and postpartum metabolite levels were higher in these Salinas Valley women than in a sample of women of childbearing age in the general U.S. population (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey), although the deviation from U.S. reference levels was most pronounced after delivery. Higher DAP metabolite levels in the immediate postpartum period may have implications for estimating dose during pregnancy and for exposure during lactation.
Figures
References
-
- Adgate JL, Kukowski A, Stroebel C, Shubat PJ, Morrell S, Quackenboss JJ, et al. Pesticide storage and use patterns in Minnesota households with children. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol. 2000;10(2):159–167. - PubMed
-
- Barr DB, Barr JR, Driskell WJ, Hill RH, Ashley DL, Needham LL, et al. Strategies for biological monitoring of exposure for contemporary-use pesticides. Toxicol Ind Health. 1999;15(1–2):168–179. - PubMed
-
- Becker JG, Whitworth JA, Kincaid-Smith P. 1992. Clinical Nephrology in Medical Practice. Boston:Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

