Health disparities and toxicant exposure of Akwesasne Mohawk young adults: a partnership approach to research
- PMID: 16330372
- PMCID: PMC1314929
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.7914
Health disparities and toxicant exposure of Akwesasne Mohawk young adults: a partnership approach to research
Abstract
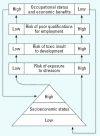
In this article we describe a research partnership between the Akwesasne Mohawk Nation and scientists at the University at Albany, State University of New York, initiated to address community and scientific concerns regarding environmental contamination and its health consequences (thyroid hormone function, social adjustment, and school functioning). The investigation focuses on cultural inputs into health disparities. It employs a risk-focusing model of biocultural interaction: behaviors expressing cultural identity and values allocate or focus risk, in this instance the risk of toxicant exposure, which alters health status through the effects of toxicants. As culturally based behaviors and activities fulfill a key role in the model, accurate assessment of subtle cultural and behavioral variables is required and best accomplished through integration of local expert knowledge from the community. As a partnership project, the investigation recognizes the cultural and socioeconomic impacts of research in small communities beyond the production of scientific knowledge. The components of sustainable partnerships are discussed, including strategies that helped promote equity between the partners such as hiring community members as key personnel, integrating local expertise into research design, and developing a local Community Outreach and Education Program. Although challenges arose during the design and implementation of the research project, a collaborative approach has benefited the community and facilitated research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A partnership study of PCBs and the health of Mohawk youth: lessons from our past and guidelines for our future.Environ Health Perspect. 1998 Jun;106 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):833-40. doi: 10.1289/ehp.98106833. Environ Health Perspect. 1998. PMID: 9646046 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing biocultural models by working with communities: a partnership approach.Am J Hum Biol. 2007 Jul-Aug;19(4):511-24. doi: 10.1002/ajhb.20611. Am J Hum Biol. 2007. PMID: 17546616
-
Relationship of lead, mercury, mirex, dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene, hexachlorobenzene, and polychlorinated biphenyls to timing of menarche among Akwesasne Mohawk girls.Pediatrics. 2005 Feb;115(2):e127-34. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1161. Epub 2005 Jan 14. Pediatrics. 2005. PMID: 15653789
-
Community health outreach program of the Chad-Cameroon petroleum development and pipeline project.Clin Occup Environ Med. 2004 Feb;4(1):9-26. doi: 10.1016/j.coem.2003.09.004. Clin Occup Environ Med. 2004. PMID: 15043361 Review.
-
A critical review of an authentic and transformative environmental justice and health community--university partnership.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014 Dec 11;11(12):12817-34. doi: 10.3390/ijerph111212817. Print 2014 Dec. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014. PMID: 25514142 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A State-of-the-Art Review of Indigenous Peoples and Environmental Pollution.Integr Environ Assess Manag. 2020 May;16(3):324-341. doi: 10.1002/ieam.4239. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Integr Environ Assess Manag. 2020. PMID: 31863549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collaboration versus communication: The Department of Energy's Amchitka Island and the Aleut Community.Environ Res. 2009 May;109(4):503-10. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2009.01.002. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Environ Res. 2009. PMID: 19264301 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Related Participatory Research in American Indian and Alaska Native Communities: A Scoping Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Aug 18;16(16):2969. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16162969. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31426579 Free PMC article.
-
Community Protections in American Indian and Alaska Native Participatory Research-A Scoping Review.Soc Sci (Basel). 2019 Apr;8(4):127. doi: 10.3390/socsci8040127. Epub 2019 Apr 20. Soc Sci (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31463160 Free PMC article.
-
An evidence map of polychlorinated biphenyl exposure and health outcome studies among residents of the Akwesasne Mohawk Nation.Chemosphere. 2022 Nov;306:135454. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135454. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35764106 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akwesasne Notes eds. 1993. Basic Call to Consciousness. Summertown, TN:Book Publishing Company.
-
- ATFE 1996. Protocol for Review of Environmental and Scientific Research Proposals. Akwesasne Mohawk Nation, New York:Akwesasne Task Force on the Environment, Research Advisory Committee.
-
- ATFE (Akwesasne Task Force on the Environment) Superfund clean-up at Akwesasne: a case study in environmental justice. Int J Contemp Sociol. 1997;34:267–290.
-
- ATFE (Akwesasne Task Force on the Environment) and Research Advisory Committee. Akwesasne Good Mind Research Protocol. Akwesasne Notes New Ser. 1997;1:94–96.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

