Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is dispensable for normal centrosome duplication but required for oncogene-induced centrosome overduplication
- PMID: 16331279
- PMCID: PMC2225596
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209310
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is dispensable for normal centrosome duplication but required for oncogene-induced centrosome overduplication
Abstract
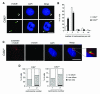
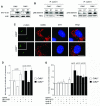
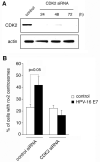
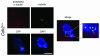
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) has been proposed to function as a master regulator of centrosome duplication. Using mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) in which Cdk2 has been genetically deleted, we show here that CDK2 is not required for normal centrosome duplication, maturation and bipolar mitotic spindle formation. In contrast, Cdk2 deficiency completely abrogates aberrant centrosome duplication induced by a viral oncogene. Mechanistically, centrosome overduplication in MEFs wild-type for Cdk2 involves the formation of supernumerary immature centrosomes. These results indicate that normal and abnormal centrosome duplication have significantly different requirements for CDK2 activity and point to a role of CDK2 in licensing centrosomes for aberrant duplication. Furthermore, our findings suggest that CDK2 may be a suitable therapeutic target to inhibit centrosome-mediated chromosomal instability in tumor cells.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

