Differential phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of beta2-adrenoceptor sites Ser262 and Ser355,356
- PMID: 16331289
- PMCID: PMC1751300
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706551
Differential phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of beta2-adrenoceptor sites Ser262 and Ser355,356
Abstract
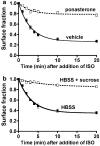
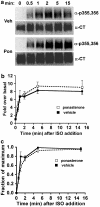
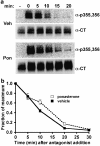
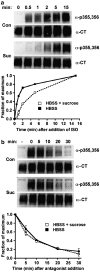
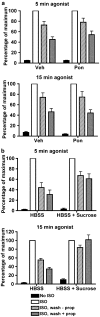
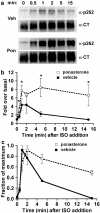
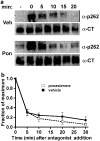
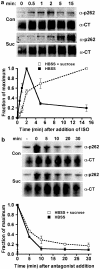
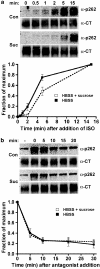
Activated beta2-adrenoceptors are rapidly desensitized by phosphorylation of Ser262 by protein kinase A (PKA) and of Ser355,356 by G-protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK). We sought to determine whether the phosphorylation and subsequent dephosphorylation of these sites had similar kinetics and requirements for receptor endocytosis. The phosphorylation of the PKA and GRK sites were measured using antibodies that recognize phosphoserine 262 and phosphoserine 355,356. Endocytosis in stably transfected HEK293 cells was blocked by inducible expression of dominant-negative dynamin-1 K44A or by treatment with hypertonic sucrose. The phosphorylation of the GRK site Ser355,356 during a 10 microM isoprenaline treatment rapidly reached a steady state, and the extent of kinetics of phosphorylation were unaffected by dynamin-1 K44A expression, and minimally by hypertonic sucrose. In contrast, phosphorylation of the PKA site Ser262 during a 10 microM isoprenaline treatment peaked after 2 min and then rapidly declined, while inhibition of endocytosis enhanced and prolonged phosphorylation. Treatment with 300 pM isoprenaline, a concentration too low to provoke endocytosis, also resulted in prolonged PKA site phosphorylation. The dephosphorylation of these sites was measured after removal of agonist. Significant dephosphorylation of phosphoserines 262 and 355,356 was observed under conditions of very low endocytosis, however dephosphorylation of the GRK site was greater if antagonist was present after removal of agonist. The results indicate that the kinetics of beta2-adrenoceptor GRK and PKA site phosphorylation are distinct and differently affected by endocytosis, and that receptor dephosphorylation can occur either at the plasma membrane or in internal compartments.
Figures
Comment in
-
G-protein-coupled receptor dephosphorylation at the cell surface.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Feb;147(3):235-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706553. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16331287 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- BROWN B.M., CARLSON B.L., ZHU X., LOLLEY R.N., CRAFT C.M. Light-driven translocation of the protein phosphatase 2A complex regulates light/dark dephosphorylation of phosducin and rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 2002;41:13526–13538. - PubMed
-
- CONG M., PERRY S.J., LIN F.T., FRASER I.D., HU L.A., CHEN W., PITCHER J.A., SCOTT J.D., LEFKOWITZ R.J. Regulation of membrane targeting of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 by protein kinase A and its anchoring protein AKAP79. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:15192–15199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

