Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is directly involved but not decisive in proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 16331492
- PMCID: PMC12161054
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-005-0060-x
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is directly involved but not decisive in proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
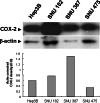
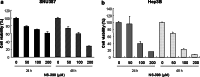
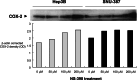
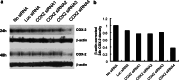
Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is involved in the chronic inflammation-related development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and the use of selective COX-2 inhibitors might provide new chemoprevention strategies for HCC. However, the role of the COX-2 in hepatocarcinogenesis remains obscure, particularly as it has been primarily studied with selective COX-2 inhibitors that may affect other cellular proteins involved in cell proliferation. Therefore, we investigated the effects of the inhibition of COX-2 by the selective COX-2 inhibitor NS-398 as well as by COX-2 specific small interfering RNA (siRNA) in the human HCC cell lines Hep3B and SNU-387. These cell lines expressed COX-2, and NS-398 induced apoptosis of these cells. NS-398 inhibited more than 60% of prostaglandin E(2) (PGE2) production and cell proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner in these cells. The inhibition of proliferation was almost restored with PGE2 supplement, suggesting that NS-398 may inhibit cell growth partially through inhibition of COX-2 and PGE2 production in human HCC cells. However, treatment with NS-398 led to increased expression of COX-2 in Hep3B and SNU-387 cells. To examine the effect of COX-2 depletion on these cells, we electroporated COX-2-specific siRNAs into SNU-387 cells. We observed significant, sequence-specific reductions in COX-2 expression, PGE2 production, and cell proliferation, though the reduction in cell proliferation was less than that induced by NS-398. In conclusion, these data suggest that COX-2 itself is directly involved, though not decisively, in proliferation of human HCC cells. RNA interference may provide a useful tool for manipulating COX-2-related hepatocarcinogenesis in research and therapeutic settings.
Figures




References
-
- Araki Y, Okamura S, Hussain SP, Nagashima M, He P, Shiseki M, Miura K, Harris CC (2003) Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by the Wnt and Ras pathways. Cancer Res 63:728–734 - PubMed
-
- Asano T, Shoda J, Ueda T, Kawamoto T, Todoroki T, Shimonishi M, Tanabe T et al (2002) Expressions of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E receptors in carcinoma of the gallbladder: crucial role of arachidonate metabolism in tumor growth and progression. Clin Cancer Res 8:1157–1167 - PubMed
-
- Bae SH, Jung ES, Park YM, Kim BS, Kim BK, Kim DG, Ryu WS (2001) Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in hepatocellular carcinoma and growth inhibition of hepatoma cell lines by a COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398. Clin Cancer Res 7:1410–1418 - PubMed
-
- Callejas NA, Castrillo A, Bosca L, Martin-Sanz P (1999) Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis up-regulates cyclooxygenase-2 indueced by lipopolysaccharide and peroxisomal proliferators. J Phar Exp Ther 288:1235–1241 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

