Engineering of solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas putida S12 for bioproduction of phenol from glucose
- PMID: 16332806
- PMCID: PMC1317433
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.12.8221-8227.2005
Engineering of solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas putida S12 for bioproduction of phenol from glucose
Abstract
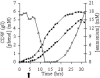
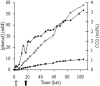
Efficient bioconversion of glucose to phenol via the central metabolite tyrosine was achieved in the solvent-tolerant strain Pseudomonas putida S12. The tpl gene from Pantoea agglomerans, encoding tyrosine phenol lyase, was introduced into P. putida S12 to enable phenol production. Tyrosine availability was a bottleneck for efficient production. The production host was optimized by overexpressing the aroF-1 gene, which codes for the first enzyme in the tyrosine biosynthetic pathway, and by random mutagenesis procedures involving selection with the toxic antimetabolites m-fluoro-dl-phenylalanine and m-fluoro-l-tyrosine. High-throughput screening of analogue-resistant mutants obtained in this way yielded a P. putida S12 derivative capable of producing 1.5 mM phenol in a shake flask culture with a yield of 6.7% (mol/mol). In a fed-batch process, the productivity was limited by accumulation of 5 mM phenol in the medium. This toxicity was overcome by use of octanol as an extractant for phenol in a biphasic medium-octanol system. This approach resulted in accumulation of 58 mM phenol in the octanol phase, and there was a twofold increase in the overall production compared to a single-phase fed batch.
Figures

References
-
- Adelberg, E. A., M. Mandel, and G. Chein Ching Chen. 1965. Optimal conditions for mutagenesis by N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 18:788-795.
-
- Adewoye, L. O., L. Tschetter, J. O'Neil, and E. A. Worobec. 1998. Channel specificity and secondary structure of the glucose-inducible porins of Pseudomonas spp. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 30:257-267. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Arias-Barrau, E., E. R. Olivera, J. M. Luengo, C. Fernandez, B. Galan, J. L. Garcia, E. Diaz, and B. Minambres. 2004. The homogentisate pathway: a central catabolic pathway involved in the degradation of l-phenylalanine, l-tyrosine, and 3-hydroxyphenylacetate in Pseudomonas putida. J. Bacteriol. 186:5062-5077. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingstom, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1987. Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing Associates, New York, N.Y.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

