Use of PCR amplification of tRNA gene-linked short tandem repeats for genotyping Entamoeba histolytica
- PMID: 16333065
- PMCID: PMC1317169
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.12.5842-5847.2005
Use of PCR amplification of tRNA gene-linked short tandem repeats for genotyping Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
We have developed a reliable method for PCR-based genotyping of Entamoeba histolytica based on variation in the numbers of short tandem repeats that are linked to tRNA genes in this species. Species-specific primer pairs were designed that differentiate E. histolytica from E. dispar as well as that reveal intraspecies PCR product length polymorphisms. The primers were tested with samples from different parts of the world, and DNA was extracted from cultured cells as well as liver abscess pus and feces by various methods. We now have the tools necessary to investigate a possible link between parasite genotype and the outcome of infection with Entamoeba histolytica, as well as other aspects of the organism's epidemiology.
Figures
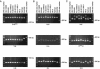
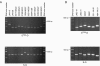
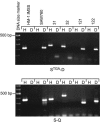
References
-
- Ayeh-Kumi, P. F., I. M. Ali, L. A. Lockhart, C. A. Gilchrist, W. A. Petri, Jr., and R. Haque.2001. Entamoeba histolytica: genetic diversity of clinical isolates from Bangladesh as demonstrated by polymorphisms in the serine-rich gene. Exp. Parasitol. 99:80-88. - PubMed
-
- Clark, C. G.1992. DNA purification from polysaccharide-rich cells, p. D-3.1-D-3.2. In J. J. Lee and A. T. Soldo (ed.), Protocols in protozoology, vol. 1. Allen Press, Lawrence, Kans.
-
- Clark, C. G., and L. S. Diamond.1993. Entamoeba histolytica: a method for isolate identification. Exp. Parasitol. 77:450-455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

