Surgical treatment of hyperparathyroidism using the quick parathyroid assay
- PMID: 16333464
- PMCID: PMC1276637
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2002.11927865
Surgical treatment of hyperparathyroidism using the quick parathyroid assay
Abstract
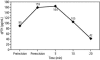
The quick intraoperative parathyroid assay (qPTH) has been proposed as an effective tool in the surgical management of hyperparathyroidism. By measuring intact parathyroid hormone intraoperatively, the qPTH assay may facilitate directed exploration for solitary adenomas and may help guide the extent of resection in hyperplasia. In this study, results of the qPTH assay were analyzed prospectively in 63 consecutive patients who underwent exploration for hyperparathyroidism. Blood samples were drawn prior to surgical incision, prior to gland excision, and 5 and 10 minutes after gland excision. A decline >/=50% of the highest preincision or preexcision level within 10 minutes of resection was considered successful. Forty-nine patients (78%) had a solitary parathyroid adenoma. The qPTH assay was successful in 48 (98%) of these patients. One patient showed a delayed decline at 20 minutes. Fourteen patients (22%) had multiglandular disease: 6 with primary hyperplasia, 4 with hyperplasia secondary to renal failure, and 4 with double adenomas. The assay was successful in all of these patients. It detected multiglandular disease in 8 of 14 patients thought preoperatively to have solitary adenoma. Overall, the qPTH assay was successful in 62 of 63 patients (98%). All patients were normocalcemic after a median follow-up interval of 8 months. These data suggest that the qPTH assay can accurately facilitate directed neck exploration for solitary adenomas, guide the extent of resection for hyperplasia, and identify unknown multiglandular disease. It appears to eliminate the most common cause of parathyroidectomy failure, thereby improving surgical success rates while potentially decreasing morbidity, cost, and operative time.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of quick parathyroid assay for uniglandular and multiglandular parathyroid disease.Am J Surg. 2002 Dec;184(6):578-81; discussion 581. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(02)01055-3. Am J Surg. 2002. PMID: 12488174
-
The validity of quick intraoperative parathyroid hormone assay: an evaluation in seventy-two patients based on gross morphologic criteria.Surgery. 1999 Dec;126(6):1030-5. doi: 10.1067/msy.2099.101833. Surgery. 1999. PMID: 10598184
-
Pitfalls of intraoperative quick parathyroid hormone monitoring and gamma probe localization in surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism.Arch Surg. 2002 Jun;137(6):659-68; discussion 668-9. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.137.6.659. Arch Surg. 2002. PMID: 12049536
-
Intraoperative quick parathyroid hormone assay in the surgical management of hyperparathyroidism.Biomed Pharmacother. 2002;56 Suppl 1:26s-30s. doi: 10.1016/s0753-3322(02)00260-3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2002. PMID: 12487246 Review.
-
The current status of intraoperative iPTH assay in surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism.Gland Surg. 2015 Feb;4(1):36-43. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2015.01.01. Gland Surg. 2015. PMID: 25713778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Appropriate surgical treatment of lithium-associated hyperparathyroidism.World J Surg. 2008 Oct;32(10):2195-9. doi: 10.1007/s00268-008-9616-7. World J Surg. 2008. PMID: 18463919
References
-
- Weber CJ, Ritchie JC. Retrospective analysis of sequential changes in serum intact parathyroid hormone levels during conventional parathyroid exploration. Surgery. 1999;126:1139–1143. - PubMed
-
- Clary BM, Garner SC, Leight GS., Jr Intraoperative parathyroid hormone monitoring during parathyroidectomy for secondary hyperparathyroidism. Surgery. 1997;122:1034–1038. - PubMed
-
- Proye CA, Carnaille B, Bizard JP, Quievreux JL, Lecomte-Houcke M. Multiglandular disease in seemingly sporadic primary hyperparathyroidism revisited: where are we in the early 1990s? A plea against unilateral parathyroid exploration. Surgery. 1992;112:1118–1122. - PubMed
-
- Bonjer HJ, Bruining HA, Birkenhager JC, Nishiyama RH, Jones MA, Bagwell CB. Single and multigland disease in primary hyperparathyroidism: clinical follow-up, histopathology, and flow cytometric DNA analysis. World J Surg. 1992;16:737–743. - PubMed
-
- Irvin GL, III, Carneiro DM. Rapid parathyroid hormone assay guided exploration. Operative Techniques in General Surgery. 1999;1:10–28.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
