Development and characterization of proteasome inhibitors
- PMID: 16338383
- PMCID: PMC2556561
- DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)99039-3
Development and characterization of proteasome inhibitors
Abstract
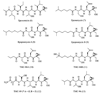
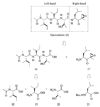
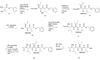
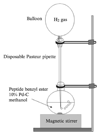
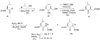
Although many proteasome inhibitors have been either synthesized or identified from natural sources, the development of more sophisticated, selective proteasome inhibitors is important for a detailed understanding of proteasome function. We have found that antitumor natural product epoxomicin and eponemycin, both of which are linear peptides containing a alpha,beta-epoxyketone pharmacophore, target proteasome for their antitumor activity. Structural studies of the proteasome-epoxomicin complex revealed that the unique specificity of the natural product toward proteasome is due to the alpha,beta-epoxyketone pharmacophore, which forms an unusual six-membered morpholino ring with the amino terminal catalytic Thr-1 of the 20S proteasome. Thus, we believe that a facile synthetic approach for alpha,beta-epoxyketone linear peptides provides a unique opportunity to develop proteasome inhibitors with novel activities. In this chapter, we discuss the detailed synthetic procedure of the alpha',beta'-epoxyketone natural product epoxomicin and its derivatives.
Figures








References
-
- Adams J. Development of the proteasome inhibitor PS-341. Oncologist. 2002;7:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Adams J, Behnke M, Chen S, Cruickshank AA, Dick LR, Grenier L, Klunder JM, Ma YT, Plamondon L, Stein RL. Potent and selective inhibitors of the proteasome: Dipeptidyl boronic acids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998;8:333–338. - PubMed
-
- Albericio F, Carpino LA. Coupling reagents and activation. Methods Enzymol. 1997;289:104–126. - PubMed
-
- Bennacer B, Rivalle C, Grierson D. A new route for the total synthesis of 6,7-dihydroeponemycin. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003;23:4569–4574.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

