Control of dendritic arborization by the phosphoinositide-3'-kinase-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin pathway
- PMID: 16339025
- PMCID: PMC6725892
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2270-05.2005
Control of dendritic arborization by the phosphoinositide-3'-kinase-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin pathway
Abstract
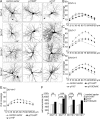
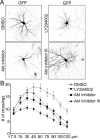
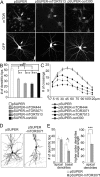
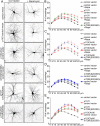
The molecular mechanisms that determine the size and complexity of the neuronal dendritic tree are unclear. Here, we show that the phosphoinositide-3' kinase (PI3K)-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway promotes the growth and branching of dendrites in cultured hippocampal neurons. Constitutively active mutants of Ras, PI3K, and Akt, or RNA interference (RNAi) knockdown of lipid phosphatase PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome Ten), induced growth and elaboration of dendrites that was blocked by mTOR inhibitor rapamycin and/or by overexpression of eIF-4E binding protein 1 (4E-BP1), which inhibits translation of 5' capped mRNAs. The effect of PI3K on dendrites was lost in more mature neurons (>14 d in vitro). Dendritic complexity was reduced by inhibition of PI3K and by RNAi knockdown of mTOR or p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (p70S6K, an effector of mTOR). A rapamycin-resistant mutant of mTOR "rescued" the morphogenetic effects of PI3K in the presence of rapamycin. By regulating global and/or local protein translation, and as a convergence point for multiple signaling pathways, mTOR could play a central role in the control of dendrite growth and branching during development and in response to activity.
Figures






References
-
- Acebes A, Ferrus A (2000) Cellular and molecular features of axon collaterals and dendrites. Trends Neurosci 23: 557–565. - PubMed
-
- Alpar A, Palm K, Schierwagen A, Arendt T, Gartner U (2003) Expression of constitutively active p21H-rasval12 in postmitotic pyramidal neurons results in increased dendritic size and complexity. J Comp Neurol 467: 119–133. - PubMed
-
- Atwal JK, Massie B, Miller FD, Kaplan DR (2000) The TrkB-Shc site signals neuronal survival and local axon growth via MEK and P13-kinase. Neuron 27: 265–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
