Arg16Gly polymorphism of the beta2-adrenergic receptor is associated with differences in cardiovascular function at rest and during exercise in humans
- PMID: 16339181
- PMCID: PMC1805638
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.098558
Arg16Gly polymorphism of the beta2-adrenergic receptor is associated with differences in cardiovascular function at rest and during exercise in humans
Abstract
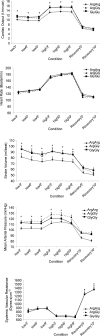
In humans, subjects homozygous for arginine (ArgArg) at codon 16 of the beta2-adrenergic receptor (beta2AR) have been shown to have greater agonist-mediated desensitization than subjects homozygous for glycine (GlyGly). We sought to determine if this substitution differentially influenced cardiovascular function during short duration (9 min) low and high intensity exercise (40 and 75% of peak work). Healthy Caucasian ArgArg (n = 16), GlyGly (n = 31) and ArgGly (n = 17) subjects matched for age, sex and peak oxygen uptake were studied. There were no differences in adrenaline (ADR) at rest or with heavy exercise, but the ArgArg group had lower ADR with light exercise (P = 0.04). Resting heart rate (HR) was higher in ArgArg (P < 0.01), while cardiac output (Q), stroke volume (SV), and mean arterial pressure (MAP) were lower than the other groups (HR = 86+/-2, 78+/-2, 80+/-1 beats min(-1); Q = 5.7+/-0.81, 6.1+/-0.18, 6.7+/-0.22 l min(-1); SV = 68+/-3, 82+/-3, 89+/-4 ml beat(-1); MAP = 92+/-1, 103+/-2, 98+/-1 mmHg-- for ArgArg, ArgGly and GlyGly, respectively, means +/-s.e.m., P < 0.01), however, no differences were observed in systemic vascular resistance (SVR). With low intensity exercise and high intensity exercise the ArgArg group continued to have a lower , SV and MAP compared to the other groups (P < 0.05), with no differences observed in SVR. During recovery, the ArgArg subjects continued to have a lower MAP but there were no differences in HR, , or SVR. These data suggest that subjects homozygous for Arg at codon 16 of the beta2AR have reduced and MAP at rest that persist during exercise with no evidence for differential changes over the course of exercise despite large changes in catecholamines. This may suggest possible genotype-related differences in baseline receptor function or density which causes phenotypic differences at rest that are sustained during short-term exercise.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Beta2-adrenergic receptor genotype and pulmonary function in patients with heart failure.Chest. 2006 Nov;130(5):1527-34. doi: 10.1378/chest.130.5.1527. Chest. 2006. PMID: 17099033
-
Genotype related differences in beta2 adrenergic receptor density and cardiac function.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006 May;38(5):882-6. doi: 10.1249/01.mss.0000218144.02831.f6. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006. PMID: 16672841
-
The Arg16/Gly beta2-adrenergic receptor polymorphism is associated with altered cardiovascular responses to isometric exercise.Physiol Genomics. 2004 Feb 13;16(3):323-8. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00152.2003. Physiol Genomics. 2004. PMID: 14665698 Clinical Trial.
-
Cardiovascular responses to exercise in children.Sports Med. 1997 Oct;24(4):241-57. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199724040-00003. Sports Med. 1997. PMID: 9339493 Review.
-
Genetics of beta2-adrenergic receptors and the cardiopulmonary response to exercise.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2008 Apr;36(2):98-105. doi: 10.1097/JES.0b013e318168f276. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2008. PMID: 18362692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How Do Antihypertensive Drugs Work? Insights from Studies of the Renal Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure.Front Physiol. 2016 Jul 29;7:320. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00320. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27524972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alveolar air and oxidative metabolic demand during exercise in healthy adults: the role of single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the β2AR gene.Physiol Rep. 2017 Nov;5(20):e13476. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13476. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29061864 Free PMC article.
-
Metoprolol Dose Equivalence in Adult Men and Women Based on Gender Differences: Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulations.Med Sci (Basel). 2016;4(4):18. doi: 10.3390/medsci4040018. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Med Sci (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28035289 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of maternal and fetal β2-adrenoceptor and nitric oxide synthase genotype on vasopressor requirement and fetal acid-base status during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery.Anesth Analg. 2011 Jun;112(6):1432-7. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182179424. Anesth Analg. 2011. PMID: 21613201 Free PMC article.
-
{beta}-Adrenoceptor gene variation and intermediate physiological traits: prediction of distant phenotype.Exp Physiol. 2010 Jul;95(7):757-64. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2009.048330. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Exp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20382665 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bernstein D. Cardiovascular and metabolic alterations in mice lacking β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors. Trends Cardiovascular Med. 2002;12:287–294. - PubMed
-
- Bittner HB, Chen EP, Milano CA, Lefkowitz RJ, Van Trigt P. Functional analysis of myocardial performance in murine hearts overexpressing the human β2-adrenergic receptor. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1997;29:961–967. - PubMed
-
- Bray MS, Krushkal J, Li L, Ferrell R, Kardia S, Sing CF, Turner ST, Boerwinkle E. Positional genomic analysis identifies the β2-adrenergic receptor gene as a susceptibility locus for human hypertension. Circulation. 2000;101:2877–2882. - PubMed
-
- Bristow MR, Hershberger RE, Port JD, Minobe W, Rasmussen R. β1- and β2-adrenergic receptor-mediated adenylate cyclase stimulation in nonfailing and failing human ventricular myocardium. Mol Pharmacol. 1989;35:295–303. - PubMed
-
- Brodde OE. β1- and β2-adrenoceptors in the human heart: properties, function, and alterations in chronic heart failure. Pharmacol Rev. 1991;43:203–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

