Gene set coregulated by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway
- PMID: 16339724
- PMCID: PMC1317485
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.4.12.2066-2077.2005
Gene set coregulated by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway
Abstract
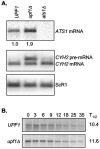
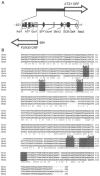
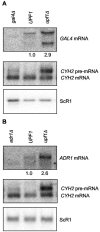
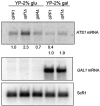
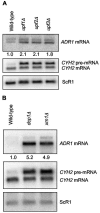
The nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) pathway has historically been thought of as an RNA surveillance system that degrades mRNAs with premature translation termination codons, but the NMD pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a second role regulating the decay of some wild-type mRNAs. In S. cerevisiae, a significant number of wild-type mRNAs are affected when NMD is inactivated. These mRNAs are either wild-type NMD substrates or mRNAs whose abundance increases as an indirect consequence of NMD. A current challenge is to sort the mRNAs that accumulate when NMD is inactivated into direct and indirect targets. We have developed a bioinformatics-based approach to address this challenge. Our approach involves using existing genomic and function databases to identify transcription factors whose mRNAs are elevated in NMD-deficient cells and the genes that they regulate. Using this strategy, we have investigated a coregulated set of genes. We have shown that NMD regulates accumulation of ADR1 and GAL4 mRNAs, which encode transcription activators, and that Adr1 is probably a transcription activator of ATS1. This regulation is physiologically significant because overexpression of ADR1 causes a respiratory defect that mimics the defect seen in strains with an inactive NMD pathway. This strategy is significant because it allows us to classify the genes regulated by NMD into functionally related sets, an important step toward understanding the role NMD plays in the normal functioning of yeast cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Physiological basis of copper tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae nonsense-mediated mRNA decay mutants.Yeast. 2013 May;30(5):179-90. doi: 10.1002/yea.2950. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Yeast. 2013. PMID: 23450501
-
Inactivation of NMD increases viability of sup45 nonsense mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.BMC Mol Biol. 2007 Aug 16;8:71. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-71. BMC Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17705828 Free PMC article.
-
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay of metal-binding activator MAC1 is dependent on copper levels and 3'-UTR length in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Curr Genet. 2024 May 6;70(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s00294-024-01291-9. Curr Genet. 2024. PMID: 38709348
-
NMD monitors translational fidelity 24/7.Curr Genet. 2017 Dec;63(6):1007-1010. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0709-4. Epub 2017 May 23. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 28536849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD)--on guard of mRNA quality].Postepy Biochem. 2006;52(4):390-8. Postepy Biochem. 2006. PMID: 17536508 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
The RNA helicase Ddx5/p68 binds to hUpf3 and enhances NMD of Ddx17/p72 and Smg5 mRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Sep;41(16):7875-88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt538. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23788676 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of functional, endogenous programmed -1 ribosomal frameshift signals in the genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(1):165-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl1033. Epub 2006 Dec 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17158156 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay on the global expression profile of budding yeast.PLoS Genet. 2006 Nov 24;2(11):e203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020203. Epub 2006 Oct 18. PLoS Genet. 2006. PMID: 17166056 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Consequences of Nonsense-Mediated Decay and Its Role in Adaptive Responses.Biomedicines. 2024 May 16;12(5):1110. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051110. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38791071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Candida albicans Tup1 is involved in farnesol-mediated inhibition of filamentous-growth induction.Eukaryot Cell. 2008 Jun;7(6):980-7. doi: 10.1128/EC.00357-07. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Eukaryot Cell. 2008. PMID: 18424510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexandre, H., V. Ansanay-Galeote, S. Dequin, and B. Blondin. 2001. Global gene expression during short-term ethanol stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 498:98-103. - PubMed
-
- Amrani, N., R. Ganesan, S. Kervestin, D. A. Mangus, S. Ghosh, and A. Jacobson. 2004. A faux 3′-UTR promotes aberrant termination and triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nature 432:112-118. - PubMed
-
- Atkin, A. L., L. R. Schenkman, M. Eastham, J. N. Dahlseid, M. J. Lelivelt, and M. R. Culbertson. 1997. Relationship between yeast polyribosomes and Upf proteins required for nonsense mRNA decay. J. Biol. Chem. 272:22163-22172. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F., R. Brent, R. Kingston, D. Moore, J. Seidman, J. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.). 2003. Current protocols in molecular biology, vol. 2, section 13. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Boston, Mass.
-
- Beelman, C. A., A. Stevens, G. Caponigro, T. E. LaGrandeur, L. Hatfield, D. M. Fortner, and R. Parker. 1996. An essential component of the decapping enzyme required for normal rates of mRNA turnover. Nature 382:642-646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

