The differential engagement of arrestin surface charges by the various functional forms of the receptor
- PMID: 16339758
- PMCID: PMC2440687
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M512148200
The differential engagement of arrestin surface charges by the various functional forms of the receptor
Abstract
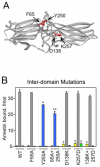
G-protein-coupled receptor signaling is terminated by arrestin proteins that preferentially bind to the activated phosphorylated form of the receptor. Arrestins also bind active unphosphorylated and inactive phosphorylated receptors. Binding to the non-preferred forms of the receptor is important for visual arrestin translocation in rod photoreceptors and the regulation of receptor signaling and trafficking by non-visual arrestins. Given the importance of arrestin interactions with the various functional forms of the receptor, we performed an extensive analysis of the receptor-binding surface of arrestin using site-directed mutagenesis. The data indicated that a large number of surface charges are important for arrestin interaction with all forms of the receptor. Arrestin elements involved in receptor binding are differentially engaged by the various functional forms of the receptor, each requiring a unique subset of arrestin residues in a specific spatial configuration. We identified several additional phosphate-binding elements in the N-domain and demonstrated for the first time that the active receptor preferentially engages the arrestin C-domain. We also found that the interdomain contact surface is important for arrestin interaction with the non-preferred forms of the receptor and that residues in this region play a role in arrestin transition into its high affinity receptor binding state.
Figures



References
-
- Ferguson SS, Downey WE, Colapietro AM, Barak LS, Menard L, Caron MG. Science. 1996;271:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Perry SJ, Lefkowitz RJ. Trends Cell Biol. 2002;12:130–138. - PubMed
-
- Gurevich VV, Gurevich EV. Structure (Camb.) 2003;11:1037–1042. - PubMed
-
- Schleicher A, Kuhn H, Hofmann KP. Biochemistry. 1989;28:1770–1775. - PubMed
-
- Palczewski K, Pulvermuller A, Buczylko J, Hofmann KP. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:18649–18654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

