Hyperlipemia and oxidation of LDL induce vascular smooth muscle cell growth: an effect mediated by the HLH factor Id3
- PMID: 16340216
- PMCID: PMC2929384
- DOI: 10.1159/000090131
Hyperlipemia and oxidation of LDL induce vascular smooth muscle cell growth: an effect mediated by the HLH factor Id3
Abstract
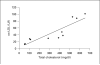
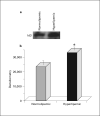
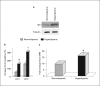
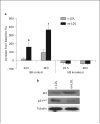
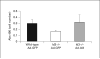
Hyperlipemia and oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) are important independent cardiovascular risk factors. Ox-LDL has been shown to stimulate vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation. However, the effects of hyperlipemia and the molecular mechanisms mediating hyperlipemia and ox-LDL effects on VSMC growth are poorly understood. The helix-loop-helix (HLH) transcription factor, Id3, is a redox-sensitive gene expressed in VSMC in response to mitogen stimulation and vascular injury. Accordingly, we hypothesize that Id3 is an important mediator of ox-LDL and hyperlipemia-induced VSMC growth. Aortas harvested from hyperlipemic pigs demonstrated significantly more Id3 than normolipemic controls. Primary VSMC were stimulated with ox-LDL, native LDL, sera from hyperlipemic pigs, or normolipemic pigs. VSMC exposed to hyperlipemic sera demonstrated increased Id3 expression, VSMC growth and S-phase entry and decreased p21cip1 expression and transcription. Cells stimulated with ox-LDL demonstrated similar findings of increased growth and Id3 expression and decreased p21cip1 expression. Moreover, the effects of ox-LDL on growth were abolished in cells devoid of the Id3 gene. Results provide evidence that the HLH factor Id3 mediates the mitogenic effect of hyperlipemic sera and ox-LDL in VSMC via inhibition of p21cip1 expression, subsequently increasing DNA synthesis and proliferation.
Figures
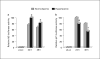
Similar articles
-
Interaction of Inhibitor of DNA binding 3 (Id3) with Gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor (GKLF) and p53 regulates proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Jan;333(1-2):33-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0201-7. Epub 2009 Jul 19. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19618124
-
Identification of a novel redox-sensitive gene, Id3, which mediates angiotensin II-induced cell growth.Circulation. 2002 May 21;105(20):2423-8. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000016047.19488.91. Circulation. 2002. PMID: 12021231
-
Redox-sensitive vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation is mediated by GKLF and Id3 in vitro and in vivo.FASEB J. 2002 Jul;16(9):1077-86. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0570com. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 12087069
-
Ceramide mediates Ox-LDL-induced human vascular smooth muscle cell calcification via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 16;8(12):e82379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082379. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24358176 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids in atherosclerosis and vascular biology.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998 Oct;18(10):1523-33. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.10.1523. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9763522 Review.
Cited by
-
E Proteins and ID Proteins: Helix-Loop-Helix Partners in Development and Disease.Dev Cell. 2015 Nov 9;35(3):269-80. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.10.019. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 26555048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Id3 is a novel atheroprotective factor containing a functionally significant single-nucleotide polymorphism associated with intima-media thickness in humans.Circ Res. 2010 Apr 16;106(7):1303-11. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.210294. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20185798 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+, calmodulin, and cyclins in vascular smooth muscle cell cycle.Circ Res. 2006 May 26;98(10):1240-3. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000225860.41648.63. Circ Res. 2006. PMID: 16728669 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Effect of Transcriptional Regulator ID3 on Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia.Int J Vasc Med. 2019 Jul 11;2019:2123906. doi: 10.1155/2019/2123906. eCollection 2019. Int J Vasc Med. 2019. PMID: 31380118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitor of differentiation-3 mediates high fat diet-induced visceral fat expansion.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Feb;32(2):317-24. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.234856. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22075252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cui Y, Blumenthal RS, Flaws JA, Whiteman MK, Langenberg P, Bachorik PS, Bush TL. Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level as a predictor of cardiovascular disease mortality. Arch Internal Med. 2001;161:1413–1419. - PubMed
-
- Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin in 20,536 high-risk individuals: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;360:7–22. - PubMed
-
- Navab M, Berliner JA, Watson AD, Hama SY, Territo MC, Lusis AJ, Shih DM, Van Lenten BJ, Frank JS, Demer LL, Edwards PA, Fogelman AM. The Yin and Yang of oxidation in the development of the fatty streak. A review based on the 1994 George Lyman Duff Memorial Lecture. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1996;16:831–842. - PubMed
-
- Stary HC, Chandler AB, Glagov S, Guyton JR, Insull W, Jr, Rosenfeld ME, Schaffer SA, Schwartz CJ, Wagner WD, Wissler RW. A definition of initial, fatty streak, and intermediate lesions of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Circulation. 1994;89:2462–2478. - PubMed
-
- Lafont A, Libby P. The smooth muscle cell: sinner or saint in restenosis and the acute coronary syndromes? J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;32:283–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

