Depression, stress, and quality of life in persons with chronic kidney disease: the Heart and Soul Study
- PMID: 16340237
- PMCID: PMC2776701
- DOI: 10.1159/000090112
Depression, stress, and quality of life in persons with chronic kidney disease: the Heart and Soul Study
Abstract
Background: The effect of mild chronic kidney disease (CKD) on depression, stress, quality of life (QOL), and health status is not well understood. We compared these outcomes in subjects with and without CKD.
Methods: We performed a cross-sectional study of 967 outpatients enrolled in the Heart and Soul Study. CKD was defined as a measured creatinine clearance < 60 ml/min. Outcome measures included depressive symptoms measured using the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ), stress measured using the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), and QOL and overall health rated as excellent, very good, good, fair, or poor.
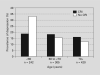
Results: The prevalence of depressive symptoms (17 vs. 19%, p = 0.4) or perceived stress (11 vs. 16%, p = 0.09) did not vary significantly by CKD. The prevalence of fair or poor QOL was not significantly different in subjects with CKD, compared with those without CKD (24 vs. 23%, p = 0.65). Age-adjusted analyses revealed a significant association of CKD with QOL (p = 0.003), however, this association no longer reached statistical significance after adjustment for confounders (p = 0.06). Subjects with CKD were more likely to report poor or fair overall health than subjects without CKD (42 vs. 34%, p = 0.03). After multivariate adjustment, CKD remained significantly associated with worse overall health (OR = 1.65, 95% CI 1.21-2.24, p = 0.001), and modestly associated with QOL (OR = 1.31, 95% CI 0.99-1.75, p = 0.06), but had no association with depression (p = 0.48) or stress (p = 0.24).
Conclusion: In this study of persons with coronary artery disease, subjects with CKD had reduced overall health and modestly reduced QOL; however, mental health was similar in those with and without CKD. These findings suggest that self- assessed overall health may decline at earlier stages of renal dysfunction than mental health outcomes or QOL.
2006 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Blake C, Codd MB, Cassidy A, O'Meara YM. Physical function, employment and quality of life in end-stage renal disease. J Nephrol. 2000;13:142–149. - PubMed
-
- Evans RW, Manninen DL, Garrison LP, Jr, Hart LG, Blagg CR, Gutman RA, Hull AR, Lowrie EG. The quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1985;312:553–559. - PubMed
-
- DeOreo PB. Hemodialysis patient-assessed functional health status predicts continued survival, hospitalization, and dialysis-attendance compliance. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997;30:204–212. - PubMed
-
- Painter P, Carlson L, Carey S, Paul SM, Myll J. Physical functioning and health-related quality-of-life changes with exercise training in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;35:482–492. - PubMed
-
- Kimmel PL, Peterson RA, Weihs KL, Simmens SJ, Alleyne S, Cruz I, Veis JH. Multiple measurements of depression predict mortality in a longitudinal study of chronic hemodialysis outpatients. Kidney Int. 2000;57:2093–2098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical