Activation of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell attenuates context-induced relapse to heroin seeking
- PMID: 16341024
- PMCID: PMC1570155
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300977
Activation of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell attenuates context-induced relapse to heroin seeking
Abstract
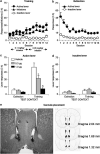
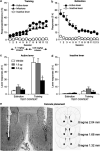
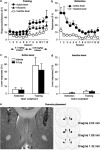
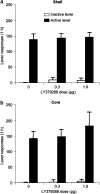
Using a rat relapse model, we previously reported that re-exposing rats to a drug-associated context, following extinction of operant responding in a different context, reinstates heroin seeking. In an initial pharmacological characterization, we found that the mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268, which acts centrally to reduce evoked glutamate release, attenuates context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking when injected systemically or into the ventral tegmental area, the cell body region of the mesolimbic dopamine system. Here, we tested whether injections of LY379268 into the nucleus accumbens (NAc), a terminal region of the mesolimbic dopamine system, would also attenuate context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. Rats were trained to self-administer heroin; drug infusions were paired with a discrete tone-light cue. Subsequently, lever pressing was extinguished in the presence of the discrete cue in a context that differed from the drug self-administration context in terms of visual, auditory, tactile, and circadian cues. After extinction of responding, LY379268 was injected to different groups of rats into the NAc core or shell or into the caudate-putamen, a terminal region of the nigrastriatal dopamine system. Injections of LY379268 into the NAc shell (0.3 or 1.0 microg) dose-dependently attenuated context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. Injections of 1.0 microg of LY379268 into the NAc core had no effect, while a higher dose (3.0 microg) decreased this reinstatement. Injections of LY379268 (3.0 microg) 1.5 mm dorsal from the NAc core into the caudate-putamen were ineffective. Results suggest an important role of glutamate transmission in the NAc shell in context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking.
Figures
References
-
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: electrophysiological properties and role in plasticity. Brain Res Rev. 1999;29:83–120. - PubMed
-
- Bardo MT, Bevins RA. Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharmacology. 2000;153:31–43. - PubMed
-
- Bast T, Zhang WN, Feldon J. The ventral hippocampus and fear conditioning in rats. Different anterograde amnesias of fear after tetrodotoxin inactivation and infusion of the GABA(A) agonist muscimol. Exp Brain Res. 2001;139:39–52. - PubMed
-
- Bossert JM, Busch RF, Gray SM. The novel mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268 attenuates cue-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. Neuroreport. 2005;16:1013–1016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

