Systematic genome-wide annotation of spliceosomal proteins reveals differential gene family expansion
- PMID: 16344558
- PMCID: PMC1356130
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.3936206
Systematic genome-wide annotation of spliceosomal proteins reveals differential gene family expansion
Abstract
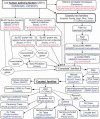
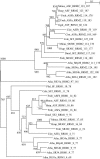
Although more than 200 human spliceosomal and splicing-associated proteins are known, the evolution of the splicing machinery has not been studied extensively. The recent near-complete sequencing and annotation of distant vertebrate and chordate genomes provides the opportunity for an exhaustive comparative analysis of splicing factors across eukaryotes. We describe here our semiautomated computational pipeline to identify and annotate splicing factors in representative species of eukaryotes. We focused on protein families whose role in splicing is confirmed by experimental evidence. We visually inspected 1894 proteins and manually curated 224 of them. Our analysis shows a general conservation of the core spliceosomal proteins across the eukaryotic lineage, contrasting with selective expansions of protein families known to play a role in the regulation of splicing, most notably of SR proteins in metazoans and of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNP) in vertebrates. We also observed vertebrate-specific expansion of the CLK and SRPK kinases (which phosphorylate SR proteins), and the CUG-BP/CELF family of splicing regulators. Furthermore, we report several intronless genes amongst splicing proteins in mammals, suggesting that retrotransposition contributed to the complexity of the mammalian splicing apparatus.
Figures


References
-
- Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W., and Lipman, D.J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215 403-410. - PubMed
-
- Amores, A., Force, A., Yan, Y.L., Joly, L., Amemiya, C., Fritz, A., Ho, R.K., Langeland, J., Prince, V., Wang, Y.L., et al. 1998. Zebrafish hox clusters and vertebrate genome evolution. Science 282 1711-1714. - PubMed
-
- Antony, A., Tang, Y.S., Khan, R.A., Biju, M.P., Xiao, X., Li, Q.J., Sun, X.L., Jayaram, H.N., and Stabler, S.P. 2004. Translational upregulation of folate receptors is mediated by homocysteine via RNA-heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein E1 interactions. J. Clin. Invest. 113 285-301. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aparicio, S., Chapman, J., Stupka, E., Putnam, N., Chia, J.M., Dehal, P., Christoffels, A., Rash, S., Hoon, S., Smit, A., et al. 2002. Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science 297 1301-1310. - PubMed
-
- Ast, G. 2004. How did alternative splicing evolve? Nat. Rev. Genet. 5 773-782. - PubMed
Web site references
-
- http://www.ensembl.org; Ensembl.
-
- http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Wise2; Wise2—Intelligent algorithms for DNA searches (EBI).
-
- http://woody.embl-heidelberg.de/gene2est; Gene2EST BLAST Server.
-
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST; NCBI BLAST.
-
- http://www.es.embnet.org/Doc/SNAP; SNAP.pl (Synonymous Nonsynonymous Analysis Program).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
