Variation in crossing-over rates across chromosome 4 of Arabidopsis thaliana reveals the presence of meiotic recombination "hot spots"
- PMID: 16344568
- PMCID: PMC1356134
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.4319006
Variation in crossing-over rates across chromosome 4 of Arabidopsis thaliana reveals the presence of meiotic recombination "hot spots"
Abstract
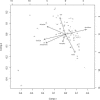
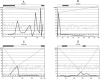
Crossover (CO) is a key process for the accurate segregation of homologous chromosomes during the first meiotic division. In most eukaryotes, meiotic recombination is not homogeneous along the chromosomes, suggesting a tight control of the location of recombination events. We genotyped 71 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) covering the entire chromosome 4 of Arabidopsis thaliana on 702 F2 plants, representing 1404 meioses and allowing the detection of 1171 COs, to study CO localization in a higher plant. The genetic recombination rates varied along the chromosome from 0 cM/Mb near the centromere to 20 cM/Mb on the short arm next to the NOR region, with a chromosome average of 4.6 cM/Mb. Principal component analysis showed that CO rates negatively correlate with the G+C content (P = 3x10(-4)), in contrast to that reported in other eukaryotes. COs also significantly correlate with the density of single repeats and the CpG ratio, but not with genes, pseudogenes, transposable elements, or dispersed repeats. Chromosome 4 has, on average, 1.6 COs per meiosis, and these COs are subjected to interference. A detailed analysis of several regions having high CO rates revealed "hot spots" of meiotic recombination contained in small fragments of a few kilobases. Both the intensity and the density of these hot spots explain the variation of CO rates along the chromosome.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson, L.K. and Stack, S.M. 2002. Meiotic recombination in plants. Curr. Genomics 3 507-525.
-
- The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. 2000. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408 796-815. - PubMed
-
- Birdsell, J.A. 2002. Integrating genomics, bioinformatics, and classical genetics to study the effects of recombination on genome evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 19 1181-1197. - PubMed
Web site references
-
- http://www.arabidopsis.org/; The Arabidopsis information resource.
-
- http://ftp.tigr.org/pub/data/a_thaliana/ath1/; Arabidopsis sequence database.
-
- http://cran.r-project.org; R software.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
