Comparing calpain- and caspase-3-mediated degradation patterns in traumatic brain injury by differential proteome analysis
- PMID: 16351572
- PMCID: PMC1383722
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20050905
Comparing calpain- and caspase-3-mediated degradation patterns in traumatic brain injury by differential proteome analysis
Abstract
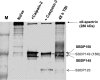
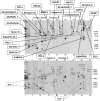
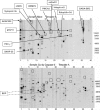
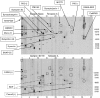
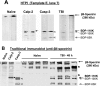
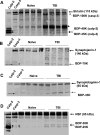
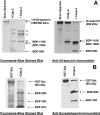
A major theme of TBI (traumatic brain injury) pathology is the over-activation of multiple proteases. We have previously shown that calpain-1 and -2, and caspase-3 simultaneously produced alphaII-spectrin BDPs (breakdown products) following TBI. In the present study, we attempted to identify a comprehensive set of protease substrates (degradome) for calpains and caspase-3. We further hypothesized that the TBI differential proteome is likely to overlap significantly with the calpain- and caspase-3-degradomes. Using a novel HTPI (high throughput immunoblotting) approach and 1000 monoclonal antibodies (PowerBlottrade mark), we compared rat hippocampal lysates from 4 treatment groups: (i) naïve, (ii) TBI (48 h after controlled cortical impact), (iii) in vitro calpain-2 digestion and (iv) in vitro caspase-3 digestion. In total, we identified 54 and 38 proteins that were vulnerable to calpain-2 and caspase-3 proteolysis respectively. In addition, the expression of 48 proteins was down-regulated following TBI, whereas that of only 9 was up-regulated. Among the proteins down-regulated in TBI, 42 of them overlapped with the calpain-2 and/or caspase-3 degradomes, suggesting that they might be proteolytic targets after TBI. We further confirmed several novel TBI-linked proteolytic substrates, including betaII-spectrin, striatin, synaptotagmin-1, synaptojanin-1 and NSF (N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein) by traditional immunoblotting. In summary, we demonstrated that HTPI is a novel and powerful method for studying proteolytic pathways in vivo and in vitro.
Figures
References
-
- Yamashima T. Implication of cysteine proteases calpain, cathepsin and caspase in ischemic neuronal death of primates. Prog. Neurobiol. 2000;62:273–295. - PubMed
-
- Asah M., Asahi K., Jung J. C., del Zoppo G. J., Fini M. E., Lo E. H. Role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 after focal cerebral ischemia, effects of gene knockout and enzyme inhibition with BB-94. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:1681–1689. - PubMed
-
- Clark A. W., Krekoski C. A., Bou S. S., Chapman K. R., Edwards D. R. Increased gelatinase A (MMP-2) and gelatinase B (MMP-9) activities in human brain after focal ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 1997;238:53–56. - PubMed
-
- Phillips J. B., Williams A. J., Adams J., Elliott P. J., Tortella F. C. Proteasome inhibitor PS519 reduces infarction and attenuates leukocyte infiltration in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2000;31:1686–1693. - PubMed
-
- Wang K. K. W. Calpain and caspase, can you tell the difference. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:20–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

