Simplified screening for the detection of soluble fusion constructs expressed in E. coli using a modular set of vectors
- PMID: 16351710
- PMCID: PMC1326211
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-4-34
Simplified screening for the detection of soluble fusion constructs expressed in E. coli using a modular set of vectors
Abstract
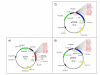
Background: The solubility of recombinant proteins expressed in bacteria is often disappointingly low. Several strategies have been developed to improve the yield and one of the most common strategies is the fusion of the target protein with a suitable partner. Despite several reports on the successful use of each of these carriers to increase the solubility of some recombinant proteins, none of them was always successful and a combinatorial approach seems more efficient to identify the optimal combination for a specific protein. Therefore, the efficiency of an expression system critically depends on the speed in the identification of the optimal combination for the suitable fusion candidate in a screening process. This paper describes a set of expression vectors (pETM) designed for rapid subcloning, expression and subsequent purification using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC).
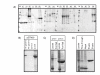
Results: A single PCR product of two Yellow Fluorescent Proteins (EYFPs) was cloned into 18 vectors comprising identical restriction sites and varying fusion partners as well as differing protease recognition sites. After a small-scale expression, the yields of the different constructs were compared using a Coomassie stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel and the results of this preliminary screening were then confirmed by large-scale purification. The yields were calculated and the stability of the different constructs determined using three independent conditions. The results indicated a significant correlation between the length and composition of non-native amino acid tails and stability. Furthermore, the buffer specificity of TEV and 3C proteases was tested using fusion proteins differing only in their protease recognition sequence, and a His-GST-EYFP construct was employed to compare the efficiency of the two alternative affinity purification methods.
Conclusion: The experiments showed that the set of pETM vectors could be used for the rapid production of a large array of different constructs with specific yield, stability, and cleavage features. Their comparison allowed the identification of the optimal constructs to use for the large-scale expression. We expect that the approach outlined in this paper, i.e. the possibility to obtain in parallel fusion products of the target protein with different partners for a preliminary evaluation, would be highly beneficial for all them who are interested in the rapid identification of the optimal conditions for protein expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A family of E. coli expression vectors for laboratory scale and high throughput soluble protein production.BMC Biotechnol. 2006 Mar 1;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-6-12. BMC Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16509985 Free PMC article.
-
Dual expression system suitable for high-throughput fluorescence-based screening and production of soluble proteins.J Proteome Res. 2005 Nov-Dec;4(6):2137-47. doi: 10.1021/pr050230i. J Proteome Res. 2005. PMID: 16335960
-
High-Level Soluble Expression and One-step Purification of HTLV-I P19 Protein in Escherichia coli by Fusion Expression.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015 Dec;14(6):624-32. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26725560
-
A modular set of prokaryotic and eukaryotic expression vectors.Anal Biochem. 2000 Jan 1;277(1):109-20. doi: 10.1006/abio.1999.4383. Anal Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10610695
-
Enhancing the solubility of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli by using hexahistidine-tagged maltose-binding protein as a fusion partner.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;705:259-74. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61737-967-3_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21125392 Review.
Cited by
-
GTP-dependent structural rearrangement of the eRF1:eRF3 complex and eRF3 sequence motifs essential for PABP binding.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(2):548-58. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp908. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19906736 Free PMC article.
-
In situ overlap and sequence synthesis during DNA assembly.ACS Synth Biol. 2013 Dec 20;2(12):750-5. doi: 10.1021/sb400067v. Epub 2013 Nov 6. ACS Synth Biol. 2013. PMID: 24161008 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Bases for the Allergenicity of Fra a 1.02 in Strawberry Fruits.J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Sep 30;68(39):10951-10961. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05714. Epub 2020 Jan 3. J Agric Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 31774998 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the ribosome-associated protein PY in the cold-shock response of Escherichia coli.Microbiologyopen. 2013 Apr;2(2):293-307. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.68. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Microbiologyopen. 2013. PMID: 23420694 Free PMC article.
-
Cofactor-independent RNA editing by a synthetic S-type PPR protein.Synth Biol (Oxf). 2021 Dec 23;7(1):ysab034. doi: 10.1093/synbio/ysab034. eCollection 2021. Synth Biol (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 35128071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- LaVallie ER, DiBlasio EA, Kovacic S, Grant KL, Schendel PF, McCoy JM. A thioredoxin gene fusion expression system that circumvents inclusion body formation in the E. coli cytoplasm. Bio Technology. 1993;11:187–193. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

