Cytokine responses in gnotobiotic pigs after infection with virulent or attenuated human rotavirus
- PMID: 16352562
- PMCID: PMC1317545
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.1.372-382.2006
Cytokine responses in gnotobiotic pigs after infection with virulent or attenuated human rotavirus
Abstract
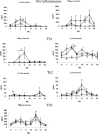
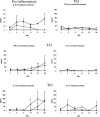
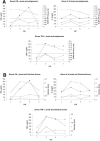
To understand the role of cytokines during rotavirus infection, we assessed the kinetics of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) (proinflammatory), IL-12 (Th1 inducer), gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) (Th1), IL-4 and IL-10 (Th2), and transforming growth factor beta (Th3) cytokine responses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in serum and intestinal contents of neonatal gnotobiotic pigs and IL-12, IFN-gamma, IL-4, and IL-10 cytokine-secreting cell (CSC) responses of mononuclear cells from ileum, spleen, and blood by ELISPOT. Pigs received the virulent Wa P1A[8]G1 strain of human rotavirus (HRV) (VirHRV), attenuated Wa HRV (AttHRV), or mock (controls). The TNF-alpha levels peaked earlier and remained elevated in serum of the VirHRV group but peaked later in the AttHRV group. In serum, IL-6 was significantly elevated at postinoculation day (PID) 1 in the VirHRV group and at PID 3 in both HRV groups. The IL-12 was detected in serum of all pigs including controls with significantly elevated peaks in both HRV-infected groups, indicating a role for IL-12 in the induction of immune responses to rotavirus infection. Only low and transient IFN-gamma responses occurred in serum and intestinal contents of the AttHRV-infected pigs, compared to significantly higher and prolonged IFN-gamma responses in the VirHRV-infected pigs. This observation coincides with the diarrhea and viremia induced by VirHRV. The number of IFN-gamma-secreting cells was significantly higher in the ileum of the VirHRV group than in that of the controls. The number of IL-4 CSCs was significantly higher in ileum of both HRV groups than in that of the controls. Significantly higher levels of IL-10 in the serum occurred early in the VirHRV group, compared to lower levels in the AttHRV group. However, the number of IL-10 CSCs was significantly higher later in ileum and spleen of the AttHRV than in the VirHRV group, suggesting a delayed initiation of a Th2 response induced by AttHRV. A significantly higher percentage of pigs had IFN-gamma and IL-10 responses in serum after VirHRV infection than after AttHRV infection or in controls. These data indicate a balanced Th1/Th2 response during rotavirus infection, with higher cytokine levels early after infection with VirHRV compared to that with AttHRV. Mapping the kinetics and patterns of cytokine responses after rotavirus infection has important implications for induction of protective immunity by HRV vaccines. Higher protection rates may be associated with more balanced Th1- and Th2-type responses, but induction of higher earlier IFN-gamma (Th1) and proinflammatory cytokines triggered by VirHRV may also play an important role in the higher intestinal immunoglobulin A responses and protection rates induced by VirHRV.
Figures
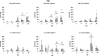
Similar articles
-
Systemic and intestinal antibody responses to NSP4 enterotoxin of Wa human rotavirus in a gnotobiotic pig model of human rotavirus disease.J Med Virol. 2002 Sep;68(1):119-28. doi: 10.1002/jmv.10178. J Med Virol. 2002. PMID: 12210439
-
Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus reuteri modulate cytokine responses in gnotobiotic pigs infected with human rotavirus.Benef Microbes. 2012 Mar 1;3(1):33-42. doi: 10.3920/BM2011.0041. Benef Microbes. 2012. PMID: 22348907 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine and antibody responses in gnotobiotic pigs after infection with human norovirus genogroup II.4 (HS66 strain).J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(17):9183-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00558-07. Epub 2007 Jun 20. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17581999 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of mucosal immune responses and protection against enteric viruses: rotavirus infection of gnotobiotic pigs as a model.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002 Sep 10;87(3-4):147-60. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(02)00046-6. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002. PMID: 12072229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The gnotobiotic piglet as a model for studies of disease pathogenesis and immunity to human rotaviruses.Arch Virol Suppl. 1996;12:153-61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6553-9_17. Arch Virol Suppl. 1996. PMID: 9015112 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effects and immunomodulation on piglets infected with rotavirus following resveratrol supplementation.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 21;13(2):e0192692. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192692. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29466421 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus modifies innate immunity and alters disease outcome in pigs subsequently infected with porcine respiratory coronavirus: implications for respiratory viral co-infections.J Gen Virol. 2009 Nov;90(Pt 11):2713-2723. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.014001-0. Epub 2009 Aug 5. J Gen Virol. 2009. PMID: 19656969 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor and innate cytokine responses induced by lactobacilli colonization and human rotavirus infection in gnotobiotic pigs.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009 Feb 15;127(3-4):304-15. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2008.10.322. Epub 2008 Oct 31. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009. PMID: 19054578 Free PMC article.
-
A protein kinase A-dependent mechanism by which rotavirus affects the distribution and mRNA level of the functional tight junction-associated protein, occludin, in human differentiated intestinal Caco-2 cells.J Virol. 2007 Aug;81(16):8579-86. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00263-07. Epub 2007 Jun 6. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17553883 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune responses to human rotavirus in the neonatal gnotobiotic piglet disease model.Immunology. 2010 Oct;131(2):242-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03298.x. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20497255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angel, J., M. A. Franco, H. B. Greenberg, and D. Bass. 1999. Lack of a role for type I and type II interferons in the resolution of rotavirus-induced diarrhea and infection in mice. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 19:655-659. - PubMed
-
- Azevedo, M. S., L. Yuan, C. Iosef, K. O. Chang, Y. Kim, T. V. Nguyen, and L. J. Saif. 2004. Magnitude of serum and intestinal antibody responses induced by sequential replicating and nonreplicating rotavirus vaccines in gnotobiotic pigs and correlation with protection. Clin. Diagn. Lab Immunol. 11:12-20. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

