Gamma interferon primes productive human immunodeficiency virus infection in astrocytes
- PMID: 16352578
- PMCID: PMC1317538
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.1.541-544.2006
Gamma interferon primes productive human immunodeficiency virus infection in astrocytes
Abstract
Considerable controversy exists over whether astrocytes can support human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. We evaluated the impact of three cytokines critical to the development of HIV neuropathogenesis, gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and tumor necrosis factor alpha, on priming astrocytes for HIV infection. We demonstrate that IFN-gamma was the most potent in its ability to facilitate substantial productive HIV infection of an astroglioma cell line (U87MG) and human fetal astrocytes (HFA). The mechanism of IFN-gamma-mediated priming of HIV in HFA is unlikely to be at the level of up-regulation of receptors and coreceptors relevant to HIV entry. These data demonstrate that cytokine priming can alter HIV replication in astrocytes.
Figures

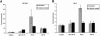
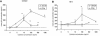

Similar articles
-
Human immunodeficiency virus-restricted replication in astrocytes and the ability of gamma interferon to modulate this restriction are regulated by a downstream effector of the Wnt signaling pathway.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):5864-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02234-06. Epub 2007 Mar 28. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17392368 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 efficiently binds to human fetal astrocytes and induces neuroinflammatory responses independent of infection.BMC Neurosci. 2007 May 12;8:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-8-31. BMC Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17498309 Free PMC article.
-
Nonproductive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of human fetal astrocytes: independence from CD4 and major chemokine receptors.Virology. 1999 Nov 25;264(2):370-84. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9998. Virology. 1999. PMID: 10562499
-
[Role of cytokines in the regulation of HIV expression].Pathol Biol (Paris). 1993 Oct;41(8 Pt 2):777-80. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1993. PMID: 8309720 Review. French.
-
Stages of restricted HIV-1 infection in astrocyte cultures derived from human fetal brain tissue.J Neurovirol. 2000 May;6 Suppl 1:S90-4. J Neurovirol. 2000. PMID: 10871771 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropathologic Findings in Elderly HIV-Positive Individuals.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2022 Jun 20;81(7):565-576. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlac040. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35656871 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic interaction between astrocytes and infiltrating PBMCs in context of neuroAIDS.Glia. 2015 Mar;63(3):441-51. doi: 10.1002/glia.22763. Epub 2014 Oct 21. Glia. 2015. PMID: 25331637 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Nef induces CCL5 production in astrocytes through p38-MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathway and utilizes NF-kB, CEBP and AP-1 transcription factors.Sci Rep. 2014 Mar 24;4:4450. doi: 10.1038/srep04450. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24658403 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders: recent advances in pathogenesis, biomarkers, and treatment.F1000Res. 2017 Mar 23;6:312. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.10651.1. eCollection 2017. F1000Res. 2017. PMID: 28413625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cocaine and HIV-1 interplay: molecular mechanisms of action and addiction.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2011 Dec;6(4):503-15. doi: 10.1007/s11481-011-9297-0. Epub 2011 Jul 16. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21766222 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Harthi, L., K. A. Roebuck, and A. Landay. 1998. Induction of HIV-1 replication by type 1-like cytokines, interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-15: effect on viral transcriptional activation, cellular proliferation, and endogenous cytokine production. J. Clin. Immunol. 18:124-131. - PubMed
-
- Balluz, I. M., M. A. Farrell, E. Kay, M. J. Staunton, J. N. Keating, O. Sheils, S. L. Cosby, M. J. Mabruk, B. J. Sheahan, and G. J. Atkins. 1996. Colocalisation of human immunodeficiency virus and human cytomegalovirus infection in brain autopsy tissue from AIDS patients. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 165:133-138. - PubMed
-
- Bezzi, P., M. Domercq, L. Brambilla, R. Galli, D. Schols, E. De Clercq, A. Vescovi, G. Bagetta, G. Kollias, J. Meldolesi, and A. Volterra. 2001. CXCR4-activated astrocyte glutamate release via TNFalpha: amplification by microglia triggers neurotoxicity. Nat. Neurosci. 4:702-710. - PubMed
-
- Boutet, A., H. Salim, Y. Taoufik, P. M. Lledo, J. D. Vincent, J. F. Delfraissy, and M. Tardieu. 2001. Isolated human astrocytes are not susceptible to infection by M- and T-tropic HIV-1 strains despite functional expression of the chemokine receptors CCR5 and CXCR4. Glia 34:165-177. - PubMed
-
- Burudi, E. M., S. Riese, P. D. Stahl, and A. Regnier-Vigouroux. 1999. Identification and functional characterization of the mannose receptor in astrocytes. Glia 25:44-55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

