Role of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium two-component system PreA/PreB in modulating PmrA-regulated gene transcription
- PMID: 16352830
- PMCID: PMC1317599
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.188.1.141-149.2006
Role of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium two-component system PreA/PreB in modulating PmrA-regulated gene transcription
Abstract
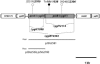
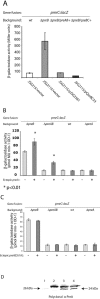
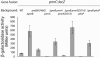
The PmrA/PmrB two-component system encoded by the pmrCAB operon regulates the modification of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium lipopolysaccharide leading to polymyxin B resistance. PmrA and PhoP are the only known activators of pmrCAB. A transposon mutagenesis screen for additional regulators of a pmrC::MudJ fusion led to the identification of a two-component system, termed PreA/PreB (pmrCAB regulators A and B), that controls the transcription of the pmrCAB operon in response to unknown signals. The initial observations indicated that insertions in, or a deletion of, the preB sensor, but not the preA response regulator, caused upregulation of pmrCAB. Interestingly, the expression of pmrCAB was not upregulated in a preAB mutant grown in LB broth, implicating PreA in the increased expression of pmrCAB in the preB strain. This was confirmed by overexpression of preA(+) in preAB or preB backgrounds, which resulted in significant upregulation or further upregulation of pmrCAB. No such effect was observed in any tested preB(+) backgrounds. Additionally, an ectopic construct expressing a preA[D51A] allele also failed to upregulate pmrC in any of the pre backgrounds tested, which implies that there is a need for phosphorylation in the activation of the target genes. The observed upregulation of pmrCAB occurred independently of the response regulators PmrA and PhoP. Although a preB mutation led to increased transcription of pmrCAB, this did not result in a measurable effect on polymyxin B resistance. Our genetic data support a model of regulation whereby, in response to unknown signals, the PreB sensor activates PreA, which in turn indirectly upregulates pmrCAB transcription.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The biology of the PmrA/PmrB two-component system: the major regulator of lipopolysaccharide modifications.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2013;67:83-112. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155751. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23799815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and genetic characterization of PmrA-regulated genes and genes involved in polymyxin B resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2002 Dec;70(12):6770-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.12.6770-6778.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12438352 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the PreA/PreB (QseB/QseC) regulon of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.BMC Microbiol. 2009 Feb 23;9:42. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-42. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19236707 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the multidrug efflux operon acrEF by insertional activation with IS1 or IS10 elements in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium DT204 acrB mutants selected with fluoroquinolones.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Jan;49(1):289-301. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.1.289-301.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15616308 Free PMC article.
-
The Salmonella PmrAB regulon: lipopolysaccharide modifications, antimicrobial peptide resistance and more.Trends Microbiol. 2008 Jun;16(6):284-90. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2008.03.007. Epub 2008 May 6. Trends Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18467098 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-to-Cell Signaling in Escherichia coli and Salmonella.EcoSal Plus. 2014 May;6(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0002-2013. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0002-2013. EcoSal Plus. 2014. PMID: 26442936 Free PMC article.
-
RpoN-Based stapled peptides with improved DNA binding suppress Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence.RSC Med Chem. 2022 Feb 17;13(4):445-455. doi: 10.1039/d1md00371b. eCollection 2022 Apr 20. RSC Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35647551 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting QseC signaling and virulence for antibiotic development.Science. 2008 Aug 22;321(5892):1078-80. doi: 10.1126/science.1160354. Science. 2008. PMID: 18719281 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi genes involved during interaction with human macrophages by screening of a transposon mutant library.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036643. Epub 2012 May 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22574205 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of the PmrA/PmrB two-component system: the major regulator of lipopolysaccharide modifications.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2013;67:83-112. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155751. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23799815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1987. Current protocols in molecular biology, vol. 1. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y.
-
- Bijlsma, J. J., and E. A. Groisman. 2005. The PhoP/PhoQ system controls the intramacrophage type three secretion system of Salmonella enterica. Mol. Microbiol. 57:85-96. - PubMed
-
- Boyer, H. W., and D. Roulland-Dussoix. 1969. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 41:459-472. - PubMed
-
- Carroll-Portillo, A. 2004. Ph.D. thesis. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, San Antonio, Tex.
-
- Cirillo, D. M., R. H. Valdivia, D. M. Monack, and S. Falkow. 1998. Macrophage-dependent induction of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system and its role in intracellular survival. Mol. Microbiol. 30:175-188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

