Kaiso-deficient mice show resistance to intestinal cancer
- PMID: 16354691
- PMCID: PMC1317619
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.199-208.2006
Kaiso-deficient mice show resistance to intestinal cancer
Abstract
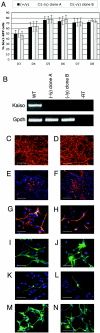
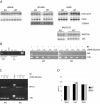
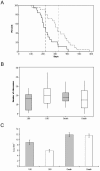
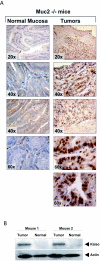
Kaiso is a BTB domain protein that associates with the signaling molecule p120-catenin and binds to the methylated sequence mCGmCG or the nonmethylated sequence CTGCNA to modulate transcription. In Xenopus laevis, xKaiso deficiency leads to embryonic death accompanied by premature gene activation in blastulae and upregulation of the xWnt11 gene. Kaiso has also been proposed to play an essential role in mammalian synapse-specific transcription. We disrupted the Kaiso gene in mice to assess its role in mammalian development. Kaiso-null mice were viable and fertile, with no detectable abnormalities of development or gene expression. However, when crossed with tumor-susceptible Apc(Min/+) mice, Kaiso-null mice showed a delayed onset of intestinal tumorigenesis. Kaiso was found to be upregulated in murine intestinal tumors and is expressed in human colon cancers. Our data suggest that Kaiso plays a role in intestinal cancer and may therefore represent a potential target for therapeutic intervention.
Figures

References
-
- Anastasiadis, P. Z., and A. B. Reynolds. 2001. Regulation of Rho GTPases by p120-catenin. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13:604-610. - PubMed
-
- Antequera, F., J. Boyes, and A. Bird. 1990. High levels of de novo methylation and altered chromatin structure at CpG islands in cell lines. Cell 62:503-514. - PubMed
-
- Chen, W. G., Q. Chang, Y. Lin, A. Meissner, A. E. West, E. C. Griffith, R. Jaenisch, and M. E. Greenberg. 2003. Derepression of BDNF transcription involves calcium-dependent phosphorylation of MeCP2. Science 302:885-889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
