Exploring the cellular activity of camptothecin-triple-helix-forming oligonucleotide conjugates
- PMID: 16354702
- PMCID: PMC1317612
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.324-333.2006
Exploring the cellular activity of camptothecin-triple-helix-forming oligonucleotide conjugates
Abstract
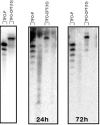
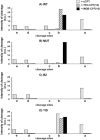
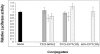
Topoisomerase I is a ubiquitous DNA-cleaving enzyme and an important therapeutic target in cancer chemotherapy for camptothecins (CPTs). These drugs stimulate DNA cleavage by topoisomerase I but exhibit little sequence preference, inducing toxicity and side effects. A convenient strategy to confer sequence specificity consists of the linkage of topoisomerase poisons to DNA sequence recognition elements. In this context, triple-helix-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) covalently linked to CPTs were investigated for the capacity to direct topoisomerase I-mediated DNA cleavage in cells. In the first part of our study, we showed that these optimized conjugates were able to regulate gene expression in cells upon the use of a Photinus pyralis luciferase reporter gene system. Furthermore, the formation of covalent topoisomerase I/DNA complexes by the TFO-CPT conjugates was detected in cell nuclei. In the second part, we elucidated the molecular specificity of topoisomerase I cleavage by the conjugates by using modified DNA targets and in vitro cleavage assays. Mutations either in the triplex site or in the DNA duplex receptor are not tolerated; such DNA modifications completely abolished conjugate-induced cleavage all along the DNA. These results indicate that these conjugates may be further developed to improve chemotherapeutic cancer treatments by targeting topoisomerase I-induced DNA cleavage to appropriately chosen genes.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Spatial organization of topoisomerase I-mediated DNA cleavage induced by camptothecin-oligonucleotide conjugates.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jul 15;31(14):4031-40. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg457. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12853620 Free PMC article.
-
Triple helix-forming oligonucleotides conjugated to indolocarbazole poisons direct topoisomerase I-mediated DNA cleavage to a specific site.Bioconjug Chem. 2001 Jul-Aug;12(4):501-9. doi: 10.1021/bc000162k. Bioconjug Chem. 2001. PMID: 11459453
-
Activation of camptothecin derivatives by conjugation to triple helix-forming oligonucleotides.Biochemistry. 2005 Mar 22;44(11):4171-80. doi: 10.1021/bi048031k. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15766244
-
Design of new anti-cancer agents based on topoisomerase poisons targeted to specific DNA sequences.Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2001 Nov;1(3):219-35. doi: 10.2174/1568011013354642. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2001. PMID: 12678755 Review.
-
Camptothecins as probes of the microenvironments of topoisomerase I--DNA complexes.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;922:76-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb07027.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 11193927 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequence-specific targeting of IGF-I and IGF-IR genes by camptothecins.FASEB J. 2010 Jul;24(7):2235-44. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-132324. Epub 2010 Feb 23. FASEB J. 2010. PMID: 20179147 Free PMC article.
-
The past and presence of gene targeting: from chemicals and DNA via proteins to RNA.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Jun 5;373(1748):20170077. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0077. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29685979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coupling the core of the anticancer drug etoposide to an oligonucleotide induces topoisomerase II-mediated cleavage at specific DNA sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Mar 16;46(5):2218-2233. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky072. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29447373 Free PMC article.
-
The triple helix: 50 years later, the outcome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Sep;36(16):5123-38. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn493. Epub 2008 Aug 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18676453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA molecular recognition and cellular selectivity of anticancer metal(II) complexes of ethylenediaminediacetate and phenanthroline: multiple targets.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2012 Jan;17(1):57-69. doi: 10.1007/s00775-011-0829-0. Epub 2011 Aug 11. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2012. PMID: 21833656
References
-
- Arimondo, P. B., C. Bailly, A. Boutorine, P. Moreau, M. Prudhomme, J. S. Sun, T. Garestier, and C. Helene. 2001. Triple helix-forming oligonucleotides conjugated to indolocarbazole poisons direct topoisomerase I-mediated DNA cleavage to a specific site. Bioconjug. Chem. 12:501-509. - PubMed
-
- Arimondo, P. B., C. Bailly, A. Boutorine, M. Prudhomme, J.-S. Sun, T. Garestier, and C. Hélène. 2000. Recognition and cleavage of DNA by rebeccamycin- or benzopyridoquinoxaline-triplex-forming oligonucleotide conjugates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8:1-8. - PubMed
-
- Arimondo, P. B., C. Bailly, A. Boutorine, V. Ryabinin, A. Syniakov, J. S. Sun, T. Garestier, and C. Helene. 2001. Directing topoisomerase I-mediated DNA cleavage to specific sites by camptothecin tethered to minor and major groove ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 40:3045-3048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
