Regulation of CD44 alternative splicing by SRm160 and its potential role in tumor cell invasion
- PMID: 16354706
- PMCID: PMC1317625
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.362-370.2006
Regulation of CD44 alternative splicing by SRm160 and its potential role in tumor cell invasion
Abstract
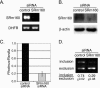
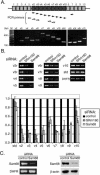
The multiple isoforms of the transmembrane glycoprotein CD44 are produced by alternative RNA splicing. Expression of CD44 isoforms containing variable 5 exon (v5) correlates with enhanced malignancy and invasiveness of some tumors. Here we demonstrate that SRm160, a splicing coactivator, regulates CD44 alternative splicing in a Ras-dependent manner. Overexpression of SRm160 stimulates inclusion of CD44 v5 when Ras is activated. Conversely, small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated silencing of SRm160 significantly reduces v5 inclusion. Immunoprecipitation shows association of SRm160 with Sam68, a protein that also stimulates v5 inclusion in a Ras-dependent manner, suggesting that these two proteins interact to regulate CD44 splicing. Importantly, siRNA-mediated depletion of CD44 v5 decreases tumor cell invasion. Reduction of SRm160 by siRNA transfection downregulates the endogenous levels of CD44 isoforms, including v5, and correlates with a decrease in tumor cell invasiveness.
Figures



References
-
- Babic, I., A. Jakymiw, and D. J. Fujita. 2004. The RNA binding protein Sam68 is acetylated in tumor cell lines, and its acetylation correlates with enhanced RNA binding activity. Oncogene 23:3781-3789. - PubMed
-
- Black, D. L. 2003. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72:291-336. - PubMed
-
- Choi, S. H., K. Takahashi, H. Eto, S. S. Yoon, and K. K. Tanabe. 2000. CD44s expression in human colon carcinomas influences growth of liver metastases. Int. J. Cancer 85:523-526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
