Few CaV1.3 channels regulate the exocytosis of a synaptic vesicle at the hair cell ribbon synapse
- PMID: 16354915
- PMCID: PMC6726013
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3411-05.2005
Few CaV1.3 channels regulate the exocytosis of a synaptic vesicle at the hair cell ribbon synapse
Abstract
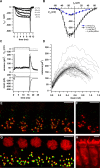
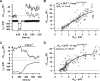
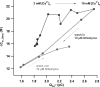
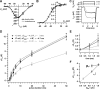
Hearing relies on faithful sound coding at hair cell ribbon synapses, which use Ca2+-triggered glutamate release to signal with submillisecond precision. Here, we investigated stimulus-secretion coupling at mammalian inner hair cell (IHC) synapses to explore the mechanisms underlying this high temporal fidelity. Using nonstationary fluctuation analysis on Ca2+ tail currents, we estimate that IHCs contain approximately 1700 Ca2+ channels, mainly of CaV1.3 type. We show by immunohistochemistry that the CaV1.3 Ca2+ channels are localized preferentially at the ribbon-type active zones of IHCs. We argue that each active zone holds approximately 80 Ca2+ channels, of which probably <10 open simultaneously during physiological stimulation. We then manipulated the Ca2+ current by primarily changing single-channel current or open-channel number. Effects on exocytosis of the readily releasable vesicle pool (RRP) were monitored by membrane capacitance recordings. Consistent with the high intrinsic Ca2+ cooperativity of exocytosis, RRP exocytosis changed nonlinearly with the Ca2+ current when varying the single-channel current. In contrast, the apparent Ca2+ cooperativity of RRP exocytosis was close to unity when primarily manipulating the number of open channels. Our findings suggest a Ca2+ channel-release site coupling in which few nearby CaV1.3 channels impose high nanodomain [Ca2+] on release sites in IHCs during physiological stimulation. We postulate that the IHC ribbon synapse uses this Ca2+ nanodomain control of exocytosis to signal with high temporal precision already at low sound intensities.
Figures

References
-
- Augustine GJ, Adler EM, Charlton MP (1991) The calcium signal for transmitter secretion from presynaptic nerve terminals. Ann NY Acad Sci 635: 365–381. - PubMed
-
- Augustine GJ, Santamaria F, Tanaka K (2003) Local calcium signaling in neurons. Neuron 40: 331–346. - PubMed
-
- Beutner D, Voets T, Neher E, Moser T (2001) Calcium dependence of exocytosis and endocytosis at the cochlear inner hair cell afferent synapse. Neuron 29: 681–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
