Visual deprivation modifies both presynaptic glutamate release and the composition of perisynaptic/extrasynaptic NMDA receptors in adult visual cortex
- PMID: 16354927
- PMCID: PMC6726025
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4362-05.2005
Visual deprivation modifies both presynaptic glutamate release and the composition of perisynaptic/extrasynaptic NMDA receptors in adult visual cortex
Abstract
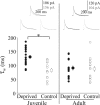
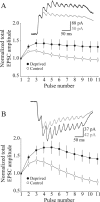
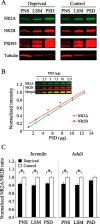
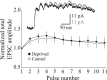
Use-dependent modifications of synapses have been well described in the developing visual cortex, but the ability for experience to modify synapses in the adult visual cortex is poorly understood. We found that 10 d of late-onset visual deprivation modifies both presynaptic and postsynaptic elements at the layer 4-->2/3 connection in the visual cortex of adult mice, and these changes differ from those observed in juveniles. Although visual deprivation in juvenile mice modifies the subunit composition and increases the current duration of synaptic NMDA receptors (NMDARs), no such effect is observed at synapses between layer 4 and layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in adult mice. Surprisingly, visual deprivation in adult mice enhances the temporal summation of NMDAR-mediated currents induced by bursts of high-frequency stimulation. The enhanced temporal summation of NMDAR-mediated currents in deprived cortex could not be explained by a reduction in the rate of synaptic depression, because our data indicate that late-onset visual deprivation actually increases the rate of synaptic depression. Biochemical and electrophysiological evidence instead suggest that the enhanced temporal summation in adult mice could be accounted for by a change in the molecular composition of NMDARs at perisynaptic/extrasynaptic sites. Our data demonstrate that the experience-dependent modifications observed in the adult visual cortex are different from those observed during development. These differences may help to explain the unique consequences of sensory deprivation on plasticity in the developing versus mature cortex.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Visual experience and deprivation bidirectionally modify the composition and function of NMDA receptors in visual cortex.Neuron. 2001 Jan;29(1):157-69. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00187-8. Neuron. 2001. PMID: 11182088
-
Synapse-specific control of experience-dependent plasticity by presynaptic NMDA receptors.Neuron. 2014 Aug 20;83(4):879-93. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.07.039. Neuron. 2014. PMID: 25144876 Free PMC article.
-
Glycine binding sites of presynaptic NMDA receptors may tonically regulate glutamate release in the rat visual cortex.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Jan;97(1):817-23. doi: 10.1152/jn.00980.2006. Epub 2006 Nov 8. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17093111
-
Presynaptic NMDA receptors: newly appreciated roles in cortical synaptic function and plasticity.Neuroscientist. 2008 Dec;14(6):609-25. doi: 10.1177/1073858408322675. Neuroscientist. 2008. PMID: 19029059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perisynaptic asymmetry of glia: new insights into glutamate signalling.Trends Neurosci. 2002 Oct;25(10):492-4. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(02)02230-0. Trends Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12220870 Review.
Cited by
-
A quantitative method to assess extrasynaptic NMDA receptor function in the protective effect of synaptic activity against neurotoxicity.BMC Neurosci. 2008 Jan 24;9:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-11. BMC Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18218077 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of visual training for full recovery from severe amblyopia in adults.Learn Mem. 2016 Jan 19;23(2):99-103. doi: 10.1101/lm.040295.115. Print 2016 Feb. Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 26787781 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive visual stimulation enhances recovery from severe amblyopia.Learn Mem. 2013 May 16;20(6):311-7. doi: 10.1101/lm.030361.113. Learn Mem. 2013. PMID: 23685763 Free PMC article.
-
Conductive hearing loss disrupts synaptic and spike adaptation in developing auditory cortex.J Neurosci. 2007 Aug 29;27(35):9417-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1992-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17728455 Free PMC article.
-
Visual deprivation modifies glutamate receptor expression in visual and auditory centers.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Dec 15;11(12):7523-7537. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31934298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birnbaum MH, Koslowe K, Sanet R (1977) Success in amblyopia therapy as a function of age: a literature survey. Am J Optom Physiol Opt 54: 269–275. - PubMed
-
- Buonomano DV, Merzenich MM (1998) Cortical plasticity: from synapses to maps. Annu Rev Neurosci 21: 149–186. - PubMed
-
- Carmignoto G, Vicini S (1992) Activity-dependent decrease in NMDA receptor responses during development of the visual cortex. Science 258: 1007–1011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
