Small ubiquitin-like modifying protein isopeptidase assay based on poliovirus RNA polymerase activity
- PMID: 16356462
- PMCID: PMC2094218
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2005.11.001
Small ubiquitin-like modifying protein isopeptidase assay based on poliovirus RNA polymerase activity
Abstract
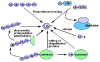
The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is the major nonlysosomal proteolytic system in eukaryotic cells responsible for regulating the level of many key regulatory molecules within the cells. Modification of cellular proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins, such as small ubiquitin-like modifying protein (SUMO), plays an essential role in a number of biological schemes, and ubiquitin pathway enzymes have become important therapeutic targets. Ubiquitination is a dynamic reversible process; a multitude of ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases (DUBs) are responsible for the wide-ranging influence of this pathway as well as its selectivity. The DUB enzymes serve to maintain adequate pools of free ubiquitin and regulate the ubiquitination status of cellular proteins. Using SUMO fusions, a novel assay system, based on poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity, is described here. The method simplifies the isopeptidase assay and facilitates high-throughput analysis of these enzymes. The principle of the assay is the dependence of the viral polymerase on a free N terminus for activity; accordingly, the polymerase is inactive when fused at its N terminus to SUMO or any other ubiquitin-like protein. The assay is sensitive, reproducible, and adaptable to a high-throughput format for use in screens for inhibitors/activators of clinically relevant SUMO proteases and deubiquitinases.
Figures






References
-
- Ciechanover A. Ubiquitin-mediated degradation of cellular proteins: why destruction is essential for construction, and how it got from the test tube to the patient’s bed. Isr Med Assoc J. 2001;3:319–327. - PubMed
-
- Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin proteolytic system and pathogenesis of human diseases: a novel platform for mechanism-based drug targeting. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:474–481. - PubMed
-
- Adams J. Preclinical and clinical evaluation of proteasome inhibitor PS-341 for the treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2002;6:493–500. - PubMed
-
- Melchior F. SUMO: Nonclassical ubiquitin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:591–626. - PubMed
-
- Hochstrasser M. Evolution and function of ubiquitin-like protein–conjugation systems. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:E153–E157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

