Attenuation of host defense function of lung phagocytes in young cystic fibrosis patients
- PMID: 16356787
- PMCID: PMC1764441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcf.2005.11.001
Attenuation of host defense function of lung phagocytes in young cystic fibrosis patients
Abstract
Background: Recent reports suggest that endotoxin exposure can blunt phagocyte functions. The aim of this study was to examine whether lung phagocytic cells have altered host defense function in young cystic fibrosis (CF) patients, and to explore the contribution of neutrophil elastase (NE) and surfactant proteins to these effects.
Methods: BALF cells from CF children (N=12) and disease controls (N=12) were analyzed by flow cytometry for mCD14 and HLA-DR expression and phagocytosis. The effects of exogenous surfactant protein A and D (SP-A,D) and proteases on BALF cells in short term culture were assessed experimentally.
Results: Expression of the surface markers mCD14 and HLA-DR, and phagocytosis, were all blunted on CF phagocytes compared to disease controls (p<0.05). In CF phagocytes, SP-A enhanced both phagocytosis and mCD14 expression (p<0.05). Both CF BALF and NE reduced phagocytosis and expression of mCD14 and HLA-DR (p<0.05) by non-CF phagocytes; the latter effect was attenuated by protease inhibitor.
Conclusion: CF airway phagocytes appear to have altered host defense functions that could contribute to poor bacterial clearance. These impairments can be reproduced by incubation of non-CF cells with NE, while SP-A can partially reverse them. Decreasing protease activity and increasing collectin activity may be beneficial in early CF.
Figures
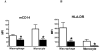
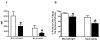
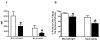
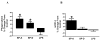


References
-
- Chmiel JF, Berger M, Konstan MW. The role of inflammation in the pathophysiology of CF lung disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2002;23:5–27. - PubMed
-
- Bruce MC, Poncz L, Klinger JD, Stern RC, Tomashefski JF, Jr, Dearborn DG. Biochemical and pathologic evidence for proteolytic destruction of lung connective tissue in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;132:529–535. - PubMed
-
- Cantin A. Cystic fibrosis lung inflammation: early, sustained, and severe. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151(4):939–941. - PubMed
-
- Doring G, Worlitzsch D. Inflammation in cystic fibrosis and its management. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2000;1(2):101–106. - PubMed
-
- Berger M. Inflammatory mediators in cystic fibrosis lung disease. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2002;23(1):19–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

