Constitutively active beta-catenin confers multilineage differentiation potential on lymphoid and myeloid progenitors
- PMID: 16356858
- PMCID: PMC1850237
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.10.009
Constitutively active beta-catenin confers multilineage differentiation potential on lymphoid and myeloid progenitors
Abstract
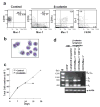
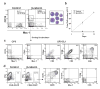
Beta-catenin-mediated Wnt signaling may contribute to the self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells and proliferation in some malignancies. We now show that expression of constitutively active beta-catenin in normal lymphoid or myeloid progenitors generated uncommitted cells with multilineage differentiation potential. Inappropriate gene expression occurred in cells destined to produce either cell type and caused corresponding changes in their characteristics. For example, forced activation of beta-catenin quickly increased C/EBPalpha while reducing EBF and Pax-5 in lymphoid progenitors that then generated myeloid cells. Inversely, EBF dramatically increased in transduced myeloid progenitors and lymphocytes were produced. The results indicate that ectopic activation of beta-catenin destabilizes lineage fate decisions and confers some, but not all, stem cell properties on committed progenitors.
Figures

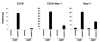


References
-
- Aasland R, Gibson TJ, Stewart AF. The PHD finger: implications for chromatin-mediated transcriptional regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:56–59. - PubMed
-
- Akashi K, Traver D, Miyamoto T, Weissman IL. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature. 2000;404:193–197. - PubMed
-
- Belenkaya TY, Han C, Standley HJ, Lin X, Houston DW, Heasman J, Lin X. pygopus Encodes a nuclear protein essential for wingless/Wnt signaling. Development. 2002;129:4089–4101. - PubMed
-
- Boggs DR. Editorial: Hematopoietic stem cell theory in relation to possible lymphoblastic conversion of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1974;44:449–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

