The RNA polymerase II subunit Rpb4p mediates decay of a specific class of mRNAs
- PMID: 16357218
- PMCID: PMC1315404
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.353205
The RNA polymerase II subunit Rpb4p mediates decay of a specific class of mRNAs
Abstract
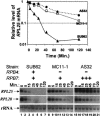
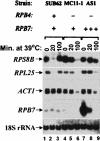
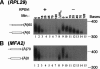
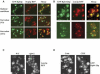
It is commonly appreciated that the mRNA level is determined by the balance between its synthetic and decay kinetics. Yet, little is known about coordination between these distinct processes. A major pathway of the eukaryotic mRNA decay initiates with shortening of the mRNA poly(A) tail (deadenylation), followed by removal of the mRNA 5' cap structure and its subsequent exonucleolytic degradation. Here we report that a subunit of RNA polymerase II, Rpb4p, is required for the decay of a class of mRNAs whose products are involved in protein synthesis. Cells lacking RPB4 are defective in the deadenylation and post-deadenylation steps of representatives of this class of mRNAs. Moreover, Rpb4p interacts with both the mRNP and with subunits of the mRNA decay complex Pat1/Lsm1-7 that enhances decapping. Consistently, a portion of Rpb4p is localized in P bodies, where mRNA decapping and degradation is executed, and mutations in RPB4 increase the number of P bodies per cell. We propose that Rpb4p has a dual function in mRNA decay. It promotes or enhances the deadenylation process of specific mRNAs and recruits Pat1/Lsm1-7 to these mRNAs, thus stimulating their decapping and further decay. In this way, Rpb4p might link the activity of the basal transcription apparatus with that of the mRNA decay machinery.
Figures




References
-
- Badis G., Saveanu, C., Fromont-Racine, M., and Jacquier, A. 2004. Targeted mRNA degradation by deadenylation-independent decapping. Mol. Cell 15: 5-15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
